
The Skinny Fat Workout & Diet Guide
Skinny fat is when you’re overfat but undermuscled, giving you a normal BMI but an unhealthy body composition. It’s when you’re not quite fat but not quite skinny, either.
The good news is you aren’t overeating or undereating, so you won’t need to force yourself to eat more food (bulking) or less food (cutting). That’s the hardest part of any physique transformation. You don’t need to worry about that. Not yet, anyway.
Instead, the best way to get rid of skinny fatness is to improve your nutrient partitioning. You need body recomposition. There are a few methods that can help with that: following a good workout program, eating a good diet, living a good lifestyle, and getting enough good sleep. Each can work on its own, but combining them all together works much better.
- What Does Skinny-Fat Mean?
- How to Know If You’re Skinny-Fat
- What Causes Skinny Fatness?
- Should You Bulk, Cut, or Recomp?
- Cardio for Skinny-Fat Guys
- The Skinny-Fat Workout
- The Skinny-Fat Diet Plan
- How to Sleep for Body Recomposition
- The Best Supplements for Skinny Fat Guys
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Does Skinny-Fat Mean?
“Skinny fat” is when you’re both under-muscled and overfat, giving you a normal BMI but a poor body composition. It’s a casual term for someone with normal-weight obesity, also known as Metabolically Obese Normal Weight (MONW).
We covered a study by Wroblewski and colleagues in our article on how age affects muscle growth (study). The researchers compared the MRI scans of people with different exercise habits, looking at their body composition:
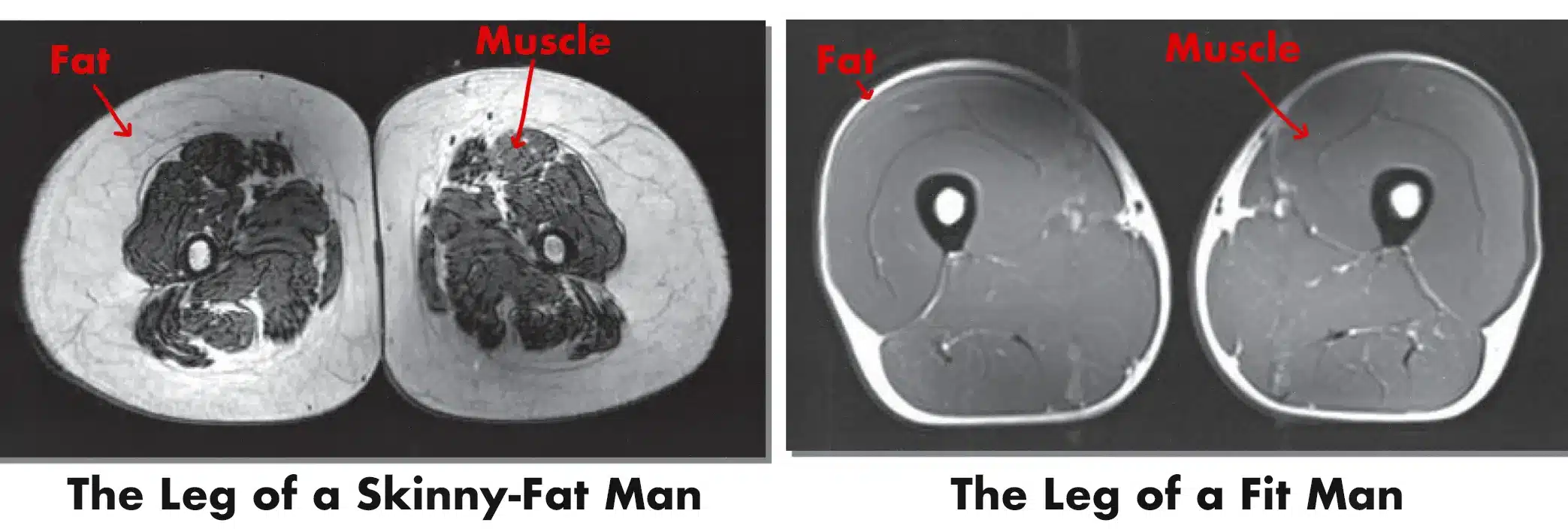
Both of these guys have legs that are about the same size, but the skinny-fat man’s leg is made of fat, whereas the fit man’s leg is made of muscle. You can see the difference in bone density, too. Look at the thick pearly white bones on the right.
Skinny fat isn’t a body type. The study found that inactivity led to simultaneous muscle loss and fat gain over time, causing people to grow gradually more skinny fat with every passing year. However, exercising allowed people to maintain their leanness and muscularity into their 70s. (There are other factors, too. More on that in a moment.)
How to Know If You’re Skinny-Fat
To figure out if you have a below-average amount of muscle mass, you can measure how big and strong you are. The average American man has 13.3-inch biceps and can bench press around 185 pounds (source). If you’re smaller or weaker than that, you’re less muscular than the average man. You might call that being skinny.
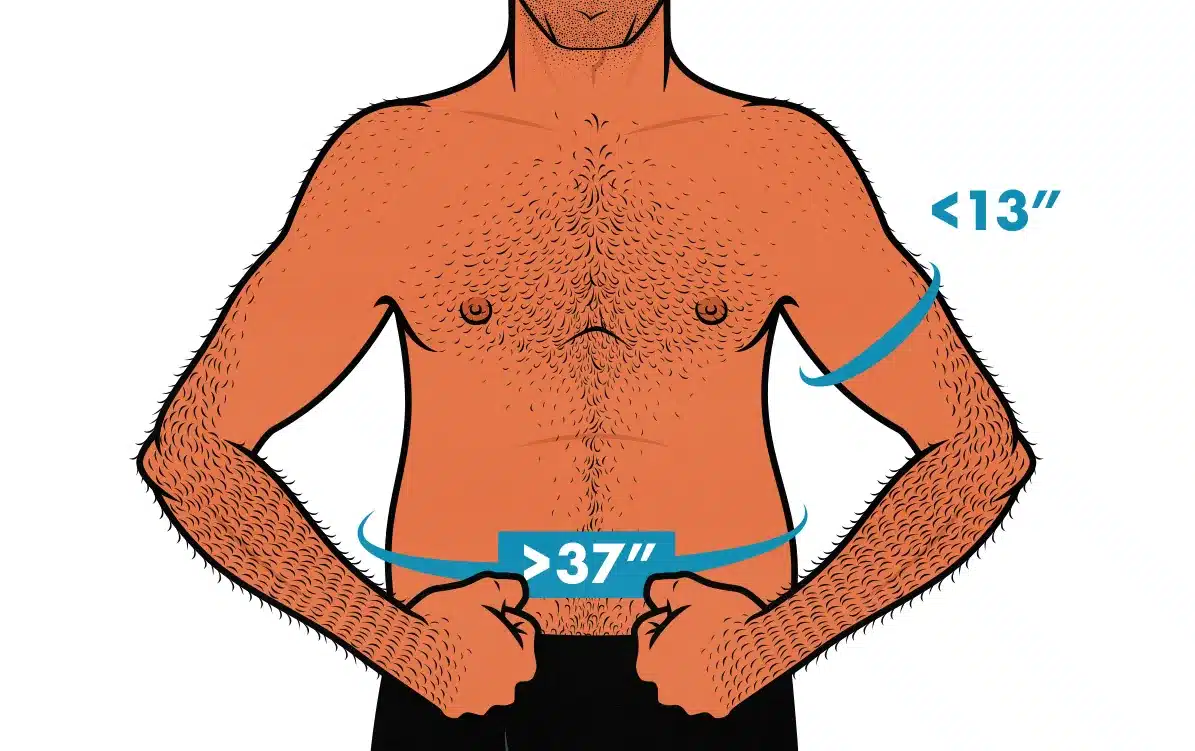
That brings us to the fat part of skinny fat. It’s common to say that 20% body fat is enough to make you skinny fat, but it’s the visceral fat underneath your abs that causes problems, so I think it makes more sense to measure your waist circumference (at the height of your belly button).
Most research shows that body fat becomes a problem when your waist circumference passes 37 or perhaps 40 inches (source). Most guys have that problem. The average American man has a waist size of 40 inches (CDC report). If your waist circumference is greater than 37 inches, you can probably improve your health by burning fat.
It’s also possible to be “thin chubby,” where you aren’t quite skinny or fat but still don’t look strong, lean, or athletic. Your situation isn’t as dire, but it can still be frustrating, and you can still use this article to build a leaner and more muscular physique.
What Causes Skinny Fatness?
Nutrient Partitioning
Skinny fatness is a problem with nutrient partitioning. Your body is storing the extra energy you eat as body fat instead of using it to build bigger muscles, denser bones, and tougher tendons.
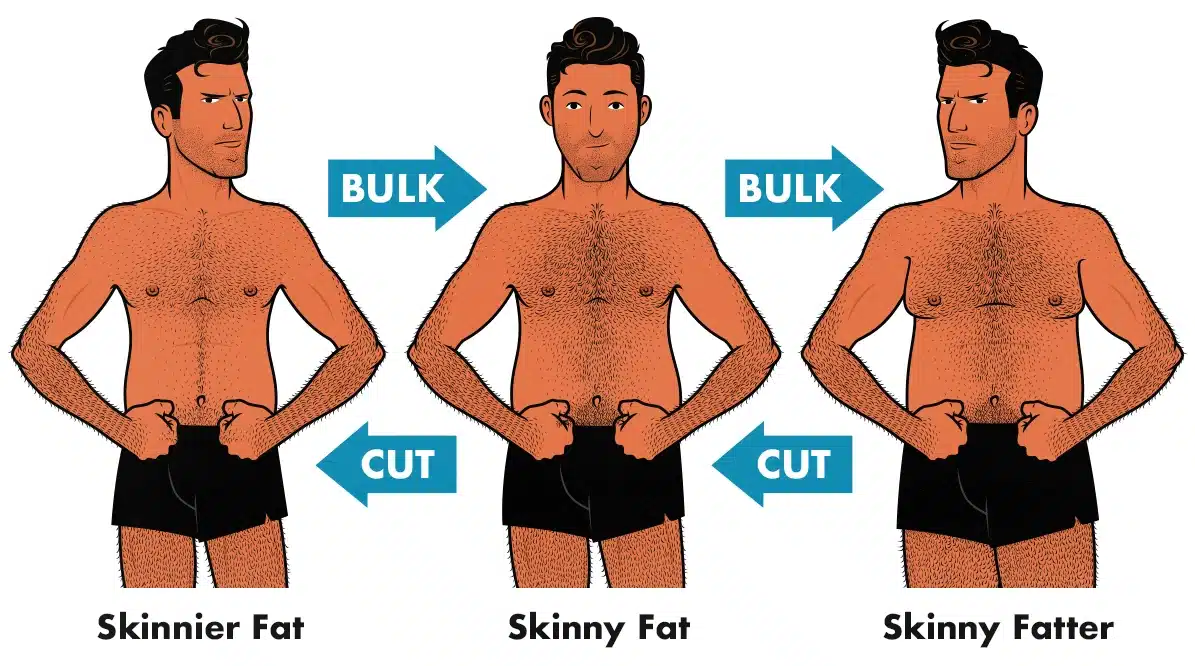
When you have poor nutrient partitioning, bulking will merely make you fatter, and cutting will only make you thinner. Neither will bring you closer to your goal. It can be incredibly frustrating.
Sometimes, it can feel like conventional advice is failing. That’s dangerous. That’s when you’re most at risk of falling into the worst trap of all—unconventional advice:
- Maybe insulin is making you skinny-fat, so you try keto.
- Maybe more growth hormone would help, so you start intermittent fasting.
- Maybe sugar is the problem, so you do a clean bulk.
There’s nothing terrible about any of those approaches, but none of them address the root issue, so none of them can fix your skinny fatness.
There’s nothing revolutionary in this article. We’ve used this same approach with professional and Olympic athletes. Your doctor will probably nod along with all of it. We aren’t trying to do things differently; we’re trying to do things correctly. That’s what produces the best results:

The good news is that when you fix your nutrient partitioning, you’ll be able to bulk more leanly, build some muscle while losing weight, or gradually improve your body composition while staying at the same weight. Once you fix your nutrient partitioning, you can destroy your skinny fatness once and for all.
Fixing the Skinny Part of Skinny-Fat
To understand the skinny part of skinny fat, it helps to look at what’s going on in your muscle fibres. The strongest predictor of someone’s response to hypertrophy training is the number of nuclei in their muscle fibres:
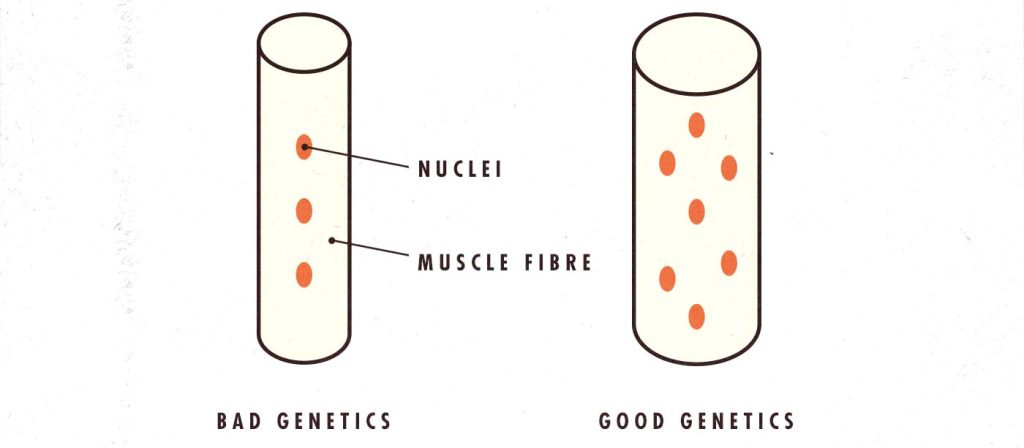
These nuclei are permanent. They don’t fade away when you stop exercising. And guys with good muscle-building genetics have more of them. Maybe they were born that way, maybe they acquired them through a childhood of being active, or maybe they gradually added them by following a rigorous workout routine. Regardless of how they got their nuclei, they have them, making it easier to gain and maintain muscle—forever.
Each of these nuclei has an area it can affect, almost like a wifi router. Your nuclei can build muscle within that area, but to go beyond, you’ll need to gain new nuclei. This partially explains “newbie gains,” where beginners build muscle quickly and then hit a plateau:
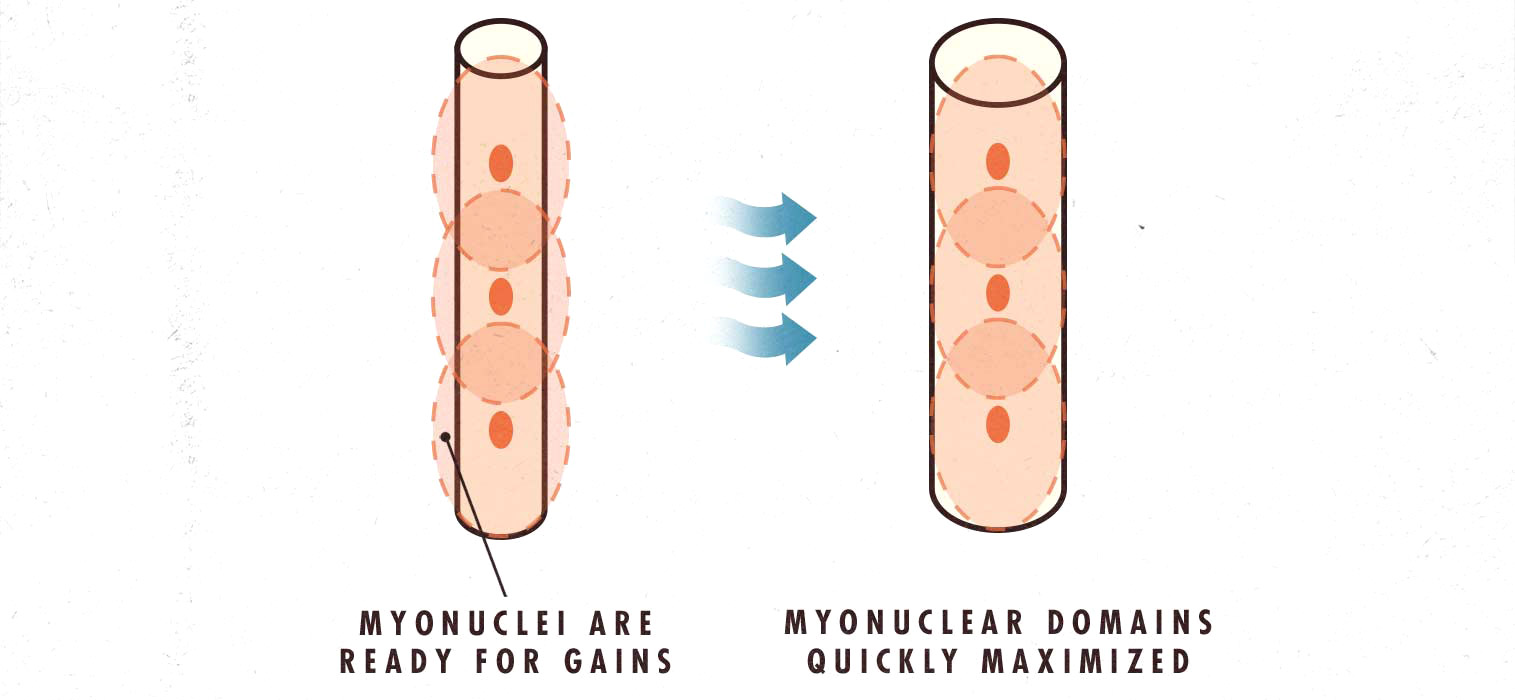
These nuclei also explain “muscle memory,” where a 43-year-old dad who hasn’t exercised since he played football in college explodes back into muscularity as soon as he touches a barbell. You might have seen some of those transformations. They’re wild.
And these nuclei shed light on the skinny-fat trap, where you gain and lose the same 10 pounds of muscle every time you bulk and cut, never accomplishing a lasting change. Your muscle fibres inflate and deflate without ever being forced to go through the arduous process of adding new nuclei. You aren’t venturing deep enough into muscle growth to make any permanent changes. But you can:
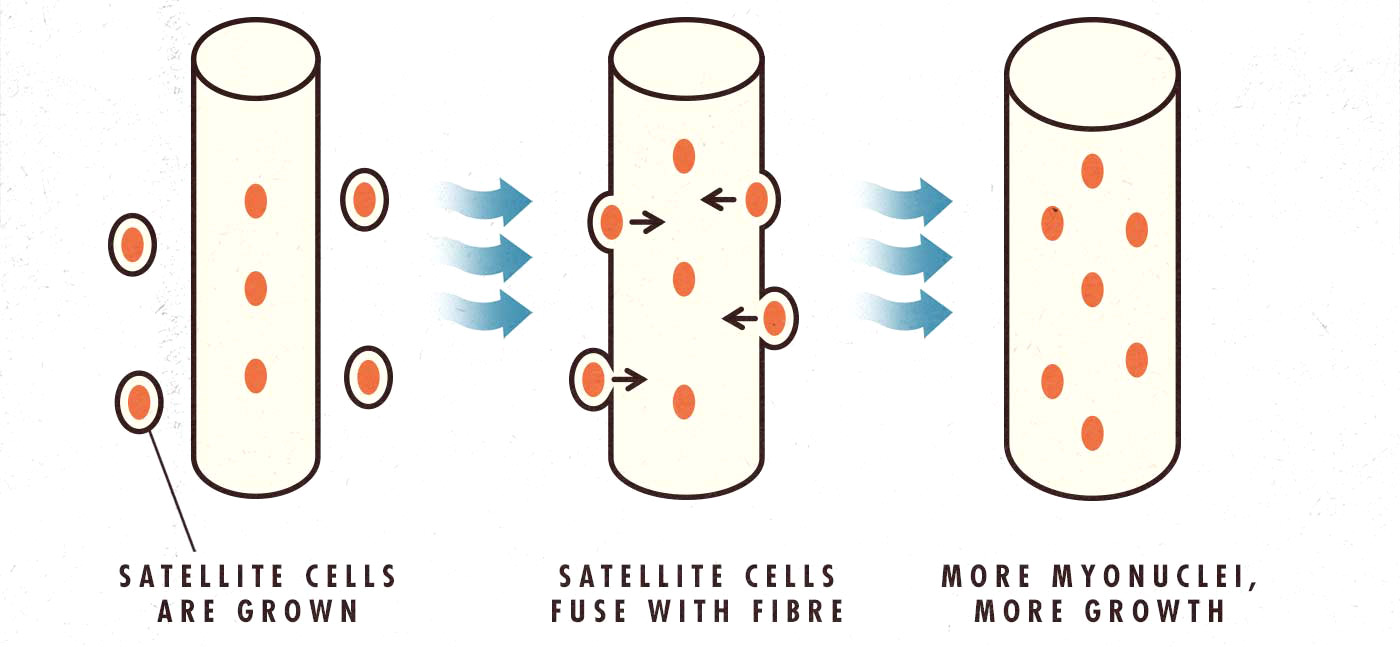
Once you’ve added these nuclei to your muscle fibres, you’ll be “naturally” more muscular for the rest of your life. If you stop working out, your muscles will still deflate, but they probably won’t ever shrink as small as they were before. And when you start lifting weights again, it will be easy to get back into peak condition.
Here’s the takeaway: If you bulk, bulk leanly, and do it for long enough to gain a significant amount of muscle and strength. The goal is to become permanently more muscular.
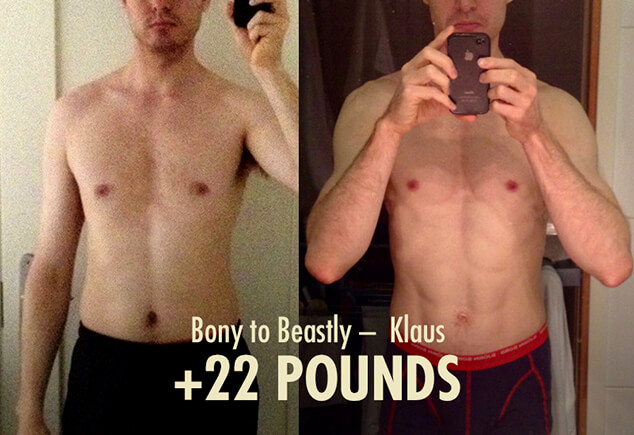

Fixing the Fat Part of Skinny-Fat
To understand the “fat” part of skinny-fat, it can help to look at your fat cells. Similar to how you can gain new nuclei in your muscle fibres, you can gain new fat cells (fat cell hyperplasia). Brad Dieter, Ph.D., talks about fat-cell hyperplasia starting to take place once people reach a BMI of about 35. For example, if you’re 5’10 and 240 pounds, gaining more fat might increase the number of fat cells you have.
Most skinny-fat guys haven’t gained extra fat cells. You probably have the same number of fat cells you’ve always had. Those fat cells are just inflated with energy. That won’t reduce your ability to get and stay leaner. In fact, it helps. The more inflated your fat cells are, the easier it is to access their energy, and so the easier it is to lose fat. In fact, you can probably use some of that energy to build muscle, achieving body recomposition.
You can’t recomp forever. When your fat cells get too deflated, they’ll grow more protective of their energy, and they’ll stop giving it up so easily. You’ll need to cut to lose fat and bulk to build muscle. I wish I could say exactly when that turning point is, but it’s different for everyone. You’ll know when you stop gaining strength on your lifts. That’s a sign you aren’t building muscle anymore.
There’s another implication that’s important for skinny-fat guys. If you cut down too lean, you’ll wind up with these ravenous fat cells that soak up every calorie you eat until you’ve regained a comfortable amount of body fat. For example, let’s say you cut down to 8% body fat (chiselled abs) and plan to do a lean bulk from there. You might not be able to. You might gain a disproportionate of fat until your body gets back up to a more comfortable 12% body fat (faint abs) or maybe even 15% body fat (flat stomach).
Here’s the takeaway: If you cut, stop before the cut gets too difficult. Keep your waist healthfully lean (under 37 inches), but don’t worry about abs until you’ve gained a significant amount of muscle and strength.
Should You Bulk, Cut, or Recomp?
Skinny fat guys have a choice. Skinny guys are underweight and under-muscled, so they benefit from bulking, sometimes quite aggressively. Fat guys are overweight, so it’s often best to focus on pure fat loss, losing weight without losing muscle. Skinny fat guys can benefit from either approach.
You also have a third option. You’re neither underweight nor overweight. Your weight isn’t a problem, so it doesn’t need to change. You can recomp.
- Lean bulk: you could start by slowly gaining weight and building muscle as leanly as possible. This works best for the skinny-fat guys who are skinnier than they are fat. It can be a good place to start if your waist circumference is well under 37 inches.
- Recomp: you could start by improving the quality of your diet, letting your appetite guide you. Your weight may not change very much. It may not change at all. But by lifting weights, being more active, eating a better diet, and living a good lifestyle, you should still be able to build muscle, gain strength, lose fat, and improve your health.
- Cutting: you could start by getting into a calorie deficit, losing weight, and focusing on burning fat. This works best for skinny-fat guys who are bordering on being overweight. This is a great place to start if your waist circumference is 40 inches or more.
As is often the case, the middle option makes for the best default. If you can’t decide whether to bulk or cut, don’t do either. Let your appetite dictate how much food you eat. You’re one of the lucky people who can do that. You’ve been eating the right amount all along.
Whatever you choose, you have to be adaptable. Start where you want, track your results, and adjust as needed. If cutting or recomping prevents you from gaining strength, you may want to gear into a lean bulk, giving your body the energy it needs to build more muscle. If you’re struggling to burn fat, you may want to veer into a cut, forcing your body to get its energy from around your gut instead of inside it.
Cardio for Skinny-Fat Guys
Cardio isn’t as powerful as lifting weights, but it can make for a very easy first step. If lifting weights seems intimidating, you can ease into a healthier routine by spending a couple of weeks getting into the routine of going on a brisk morning walk.
Cardio’s main selling point is that it’s by far the best way to improve your cardiorespiratory fitness. The other big advantage is that it’s exercise. All forms of exercise, including both cardio and lifting weights, help burn visceral fat.
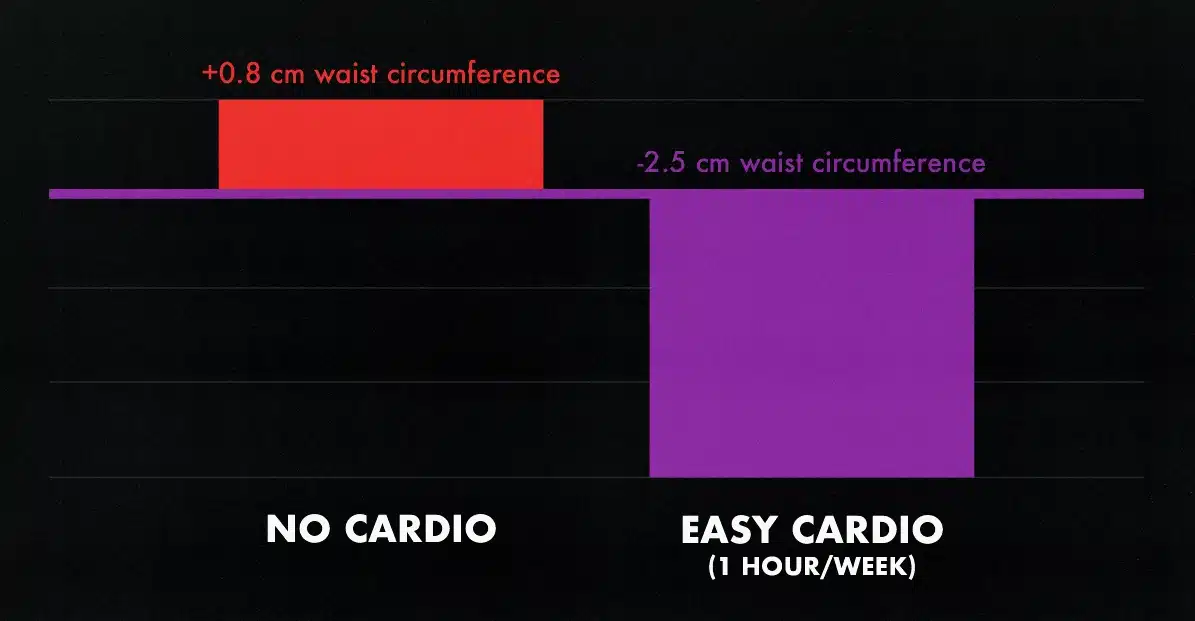
If you’re out of shape, cardio can be very simple. Going on a brisk 20-minute walk every morning is more than enough to improve your cardiovascular fitness and speed up fat loss. For example, in a study by Keating and colleagues, walking for an hour per week for 8 weeks was enough to trim an inch off the participants’ waistlines (study).
When walking becomes too easy, you can think about increasing the intensity. The simplest ways to do that are increasing the pace (jogging), increasing the load (rucking), or adding inclines and difficult terrain (hiking).
The Skinny-Fat Workout
The Importance of Resistance Training
The most powerful way to improve nutrient partitioning is to follow a rigorous hypertrophy training program—a workout program designed specifically to stimulate muscle growth. When you stimulate muscle growth, your body will prioritize building bigger muscles over storing extra energy as body fat. Any calories sent to your muscles are calories diverted away from your gut.
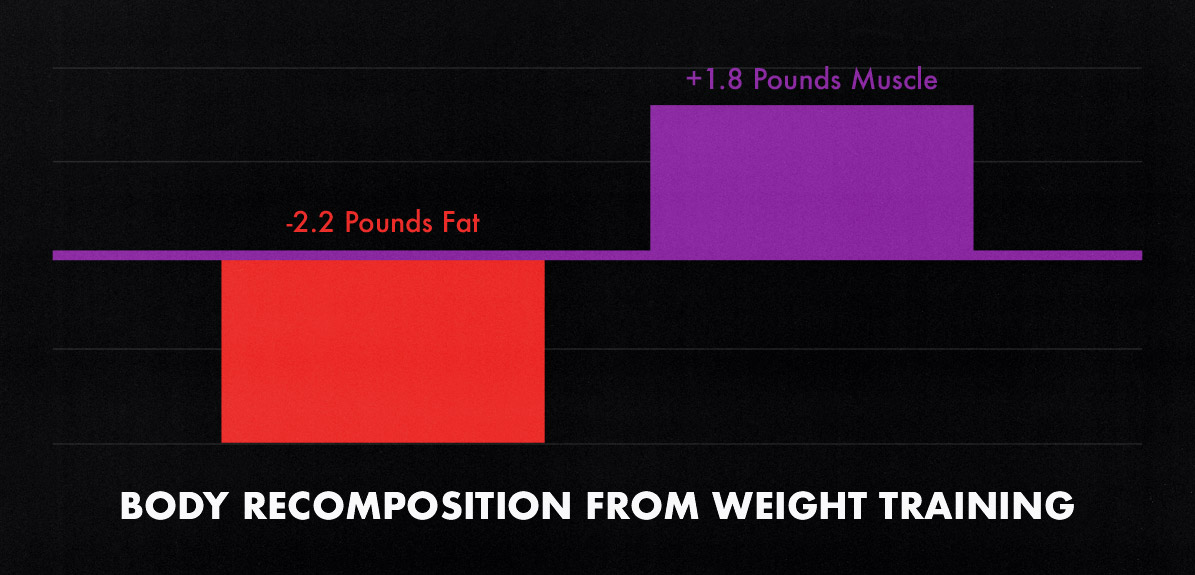
The best data we have comes from a meta-analysis of 116 studies (meta-analysis). 15 weeks of resistance training caused people to gain 1.8 pounds of muscle while losing 2.2 pounds of fat. This study included all types of resistance training (not just hypertrophy training), and the participants didn’t improve their diets or lifestyles or do any cardio. Even then, resistance training yielded body recomposition.
If you’re already in great shape, you can’t expect to get results like this. But if you’re skinny-fat, you can probably do quite a bit better, especially if you combine a good hypertrophy training workout program with the rest of the advice in this article.
The Importance of Hypertrophy Training
There are a few different types of resistance training. All of them can make you bigger, stronger, and more athletic, but each has its own specialty:
- Callisthenics is for improving your gymnastic strength and skill, giving you mastery over your body weight.
- Olympic weightlifting is for improving your explosive power, allowing you to jump higher and run faster.
- Strength training is for improving your maximal strength, allowing you to lift more weight for a single repetition.
- Hypertrophy training is for building bigger muscles (full explanation).
We recommend hypertrophy training. It’s by far the most efficient way to stimulate muscle growth. But you don’t need to be a purist about it, and you don’t need to train like a bodybuilder. After all, athletes, gymnasts, and powerlifters all use hypertrophy training to build bigger muscles. They just do it in a way that suits them.
You can use bodyweight exercises, dumbbells, barbells, exercise machines, or train at a fully stocked gym, using a fruitful mix of everything. Even if you have weights and machines, you can get better results by including some of the best callisthenics exercises: push-ups, dips, chin-ups, and pull-ups. And if you want, you can go heavier on some of your bigger exercises, developing your maximal strength.
The Basics of a Good Workout Routine
The best thing to do is follow a premade workout program, and each program has its own way of fitting all the pieces together. See what a good workout program feels like. See the results you get. From there, if you want, you can learn how to make your own workout routine.
Still, it helps to know what a good program looks like. Here are the basics:
- Focus on compound exercises. Start with beginner variations like goblet squats, push-ups, Romanian deadlifts, and lat pulldowns.
- Add isolation exercises for the muscles you’re eager to grow. For example, if you want bigger arms, add biceps curls, triceps extensions, and lateral raises (full explanation).
- Start with 3 full-body workouts per week. For example, you could do the exercises listed above every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday (full explanation).
- Do around 6–20 reps per set. Most people prefer doing 6–10 reps on the bigger compound exercises and 8–15 reps on the smaller isolation exercises (full explanation).
- Bring your sets within a rep or two of failure. It’s crucial to challenge your muscles. Take some of your sets to failure, especially on isolation exercises and on your final sets (full explanation).
- Rest for 2–3 minutes between sets. Shorter rest periods can make it harder to get enough good reps in. Longer rest periods can make your workout take far longer than it needs to (full explanation).
- Add weight or reps every workout. Fight to grow stronger, adding weight or squeezing out more repetitions whenever you’re able to. This is progressive overload, the heart of weight training (full explanation).
If you want a fully periodized 6-month workout program, including tutorial videos for every exercise, spreadsheets to fill in as you work through the program, and online help from us, check out our Bony to Beastly Program.
The Skinny-Fat Diet Plan
Hypertrophy training stimulates muscle growth, but to actually build that muscle, you need to eat enough calories and protein. It also helps to eat foods that reduce visceral fat storage. And it helps to eat a balanced diet that gives you all the micronutrients you need to thrive.
We’ll be talking about calories, but we’re just trying to give you an idea of what a balanced diet looks like. You don’t need to track your calories. You can, if you want—here’s our review of the best calorie-tracking app—but you don’t need to. You don’t have an issue with calories.
Let’s go through the full skinny-fat diet step by step.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein gives your body the building blocks it needs to build muscle. If you aren’t eating enough of it, you won’t be able to build muscle as quickly or as leanly.
If we look at this study, all of the participants were put on a hypertrophy training program and instructed to eat in a calorie deficit. Half of them ate a fairly average amount of protein (about 0.5 grams of protein per pound bodyweight), whereas the other half were instructed to eat a gram of protein per pound bodyweight per day. For a 150-pound man, that’s the difference between eating 75 grams versus 150 grams of protein per day.
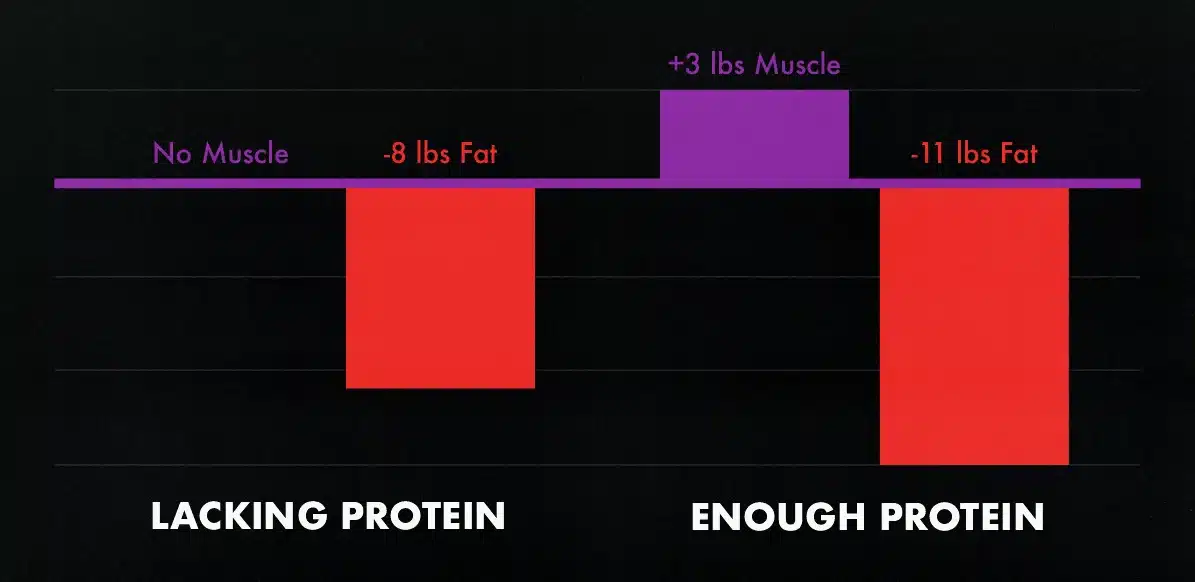
After four weeks, the participants who kept eating a typical amount of protein lost 8 pounds of fat but failed to gain a significant amount of muscle. That’s great, but the group who added protein to their diets lost 11 pounds of fat while building 3 pounds of muscle. They got body recomposition while cutting.
However, once you’re eating enough protein to build muscle, it’s no longer a limiting factor, and eating even more won’t help. The goal is to eat enough protein, not necessarily more protein.
If we look at every study, it seems that 0.7–1 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day is enough to maximize your rate of muscle growth (meta-analysis). Some people get perfect results with a little less, and some need a little more. That’s why the minimum target is a range. If you’re worried you might have bad genetics for building muscle, you could err on the higher side of that minimum intake, aiming for a full gram per pound.
How Many Carbs Should You Eat?
Carbs are fantastic for building muscle leanly. That may seem like a controversial take, especially since keto and low-carb diets are popular right now. It isn’t controversial among experts, athletes, or bodybuilders, though:
- Carbs for muscle growth: guys tend to build muscle faster and more leanly when they get 40–60% of their calories from carbohydrates (study, study). That’s standard advice for anyone trying to build muscle. It works just as well for skinny-fat guys.
- Carbs for strength and performance: The Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition recommends getting 45–55% of your calories from carbs to maximize your strength and performance (reference).
Why are carbs so good for building muscle? Carbs are a great source of energy. Your body breaks them down into glucose and stores them in your muscles as glycogen. This glycogen makes your muscles look bigger, harder, and fuller, and it fuels your workouts.
The more carbs you eat, the more glycogen you’ll store in your muscles (to a point). The more glycogen you have in your muscles, the better your workout will go, allowing you to stimulate more muscle growth. Plus, it seems that having muscles inflated with glycogen sends a signal to your body to build muscle faster (study, study, study).
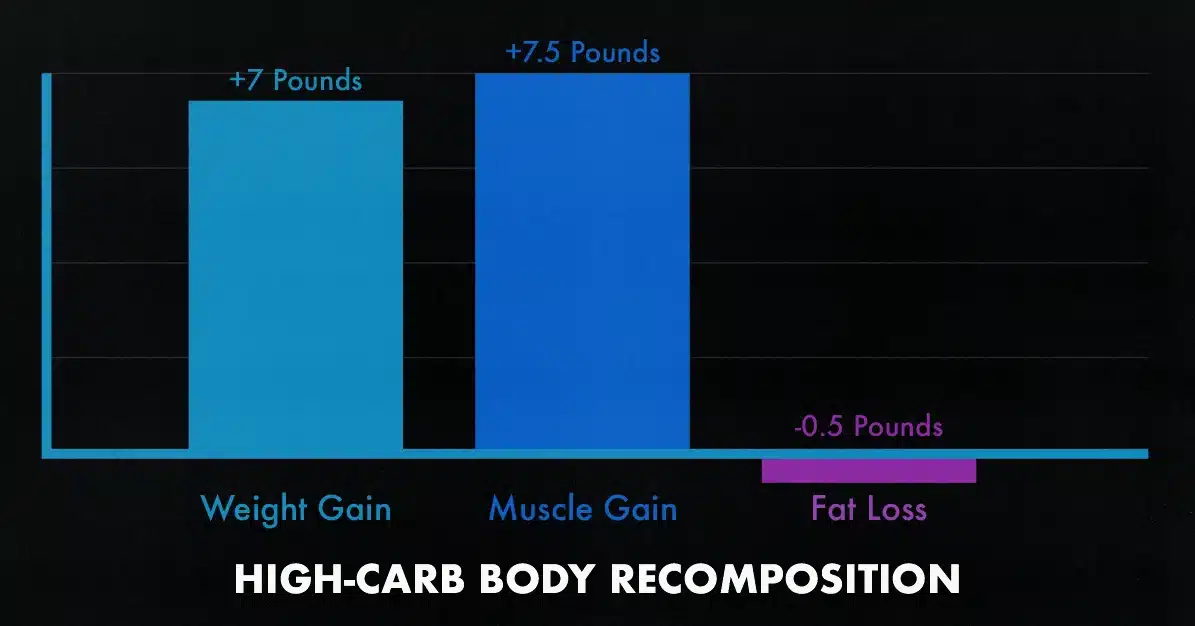
Some skinny fat guys worry that eating more carbs will cause more fat gain. That isn’t how it works. The most impressive muscle growth I’ve seen from a study came from giving the participants tons of extra carbs while following a rigorous hypertrophy training program (study). Also, keep in mind that many carbs are rich in fibre, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other important micronutrients.
Why are carbs so often demonized? Most guys have a tendency to overeat. The foods they overeat tend to be rich in both processed carbs and fats (chips, ice cream, donuts, fast food, and so on). When they remove carbs from their diets, it removes processed carbs (like soda), and it also removes foods rich in both carbs and fat. This can make it easier, sometimes, to control cravings while losing weight.
Skinny fat guys don’t have a problem with overeating. You’re over-fat, not overweight. It can definitely help to cut back on junk food, but you don’t need to remove carbs. Instead, think of eating more nutritious carbs: fruits, veggies, legumes, whole grains, oats, brown rice, potatoes, sweet potatoes, honey, and Greek yogurt.
If you have any other concerns or questions about carbs, drop a comment below. I know it can be confusing.
How Much Fat Should You Eat?
You can maximize your rate of muscle growth, fat loss, and performance with as little as 20–30% of your calories coming from dietary fat (reference). That means you probably don’t need to intentionally eat more fat. Rather, you should try to eat more nutritious fat.
Dietary fat helps to regulate hormones (including testosterone) and can be rich in important nutrients, including fat-soluble vitamins and minerals (study, study). However, not all fats are equally nutritious. Some saturated fats (butter, palm oil, and coconut oil) can harm body composition, whereas some monounsaturated fats (almonds, avocados, and olive oil) and polyunsaturated fats (walnuts, flax, and fatty fish) can improve it (study).
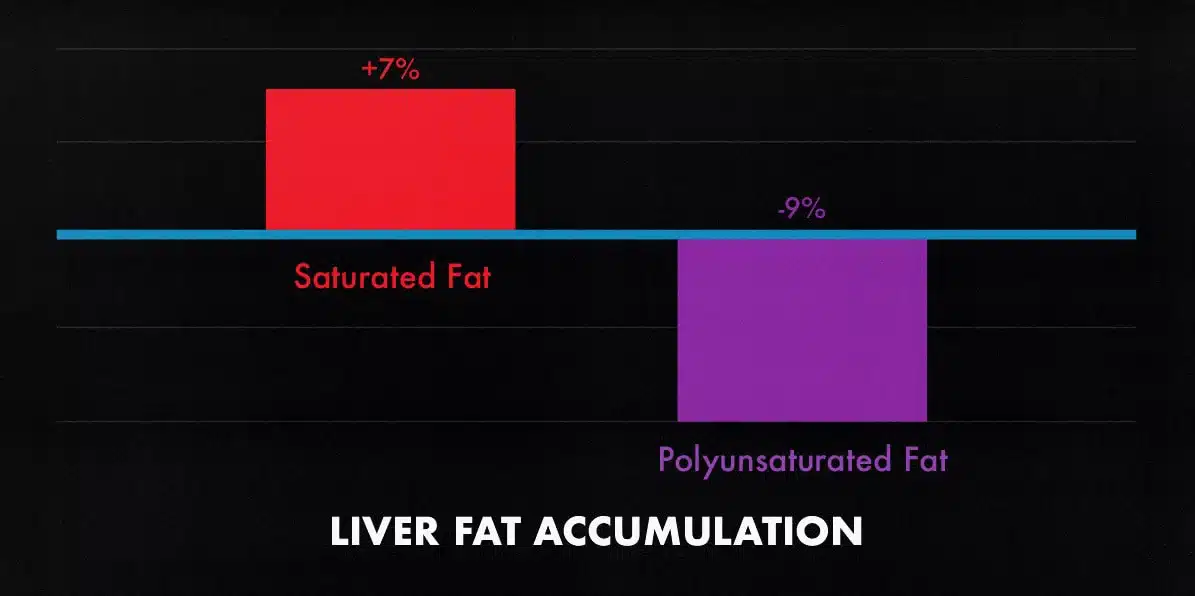
For example, in a study by Bjermo and colleagues, the participants given foods rich in butter (saturated fat) gained visceral fat, whereas the participants given foods rich in vegetable oil (polyunsaturated fat) lost visceral fat. You can do even better. You can favour even more nutritious sources of fat, such as nuts, seeds, avocados, olives, olive oil, avocado oil, fatty fish, and Greek yogurt.
Skinny-Fat Macros
The conventional muscle-building diet is high in carbs, moderate in protein, and moderate in fat, giving you macros of around 40–60% carbs, 20–30% protein, and 20–30% fat. That’s enough carbs to pump your muscles full of glycogen, enough protein to maximize your rate of muscle growth, and enough fat to regulate your hormones. For a more detailed breakdown, we have articles about how to count macros and which macros are best for building muscle.
As long as you’re somewhere in that neighbourhood, the overall quality of your diet matters more than the exact proportion of your macros. So, let’s talk about how to eat a balanced and nutritious diet.

How to Eat a Balanced Diet
A balanced bulking meal contains protein, healthy fats, nutritious carbs, fibre, and a wide variety of micronutrients. If that sounds complicated, don’t worry: most traditional meals are quite balanced. Think of chili, lentil stew, stir fry, burritos, vindaloo, baked salmon and vegetables, or the bodybuilding classic: chicken breast, rice, and broccoli drizzled with olive oil.
There are a few powerful benefits to eating balanced meals:
- Muscle growth: every time you eat a meal with a serving of protein, you’ll build a small amount of muscle.
- Regulation: fibre helps regulate blood sugar, blood lipids, and digestion.
- Nutrients: if you’re eating balanced meals, it’s much easier to get the macronutrients and micronutrients you need to support your health, fat loss, and muscle growth.
- Energy: balanced meals contain a mix of energy sources, are often easier to digest, and will probably leave you feeling better.
A balanced diet is made up of a few balanced meals per day. Those are usually spaced out fairly evenly, but there’s nothing wrong with intermittent fasting if it suits you.
To start, try to eat at least 3 balanced meals per day. When that gets easy, try to add more balance to your snacks. It doesn’t need to be difficult. Trail mix is balanced. So is Greek yogurt with frozen berries and dark chocolate chips. You could also dip apple slices into peanut butter. Maybe have some cottage cheese with fruit.
How to Eat a Nutritious Diet
We can thrive on a variety of different diets. You can eat American salmon, Scottish oats, Mexican avocados, Asian soy, African beans, Canadian blueberries, South American quinoa, Australian Macadamia nuts, and Antarctic krill.
But you don’t have to eat everything. Different cultures eat different cuisines. Within those cultures, different people prefer different foods. That’s perfectly fine. Pick the foods you like. Just make sure you have a good mix of them.
- Lean meat is high in protein and rich in vitamins and minerals. Leaner cuts are lower in saturated fat. Think of extra-lean ground meat, white fish, shrimp, and chicken breast.
- Fatty fish is high in protein and rich in omega-3s (such as EPA and DHA). These omega-3s reduce inflammation and support your overall health. Think of salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
- Eggs are high in protein and rich in healthy fats and micronutrients.
- Fermented dairy is rich in protein, calcium, and probiotics. Probiotics are great for digestion. Think of cheese, cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and kefir.
- Other fermented foods are rich in probiotics, too. Think of sauerkraut, miso, natto, tempeh, kombucha, and kimchi.
- Whole grains and legumes are nutritious starchy carbs. They’re also rich in soluble fibre, which regulates blood sugar, blood lipids, and digestion. Think of corn, quinoa, oats, beans, lentils, soybeans, peanuts, and brown rice.
- Fruits and berries are rich in vitamins, minerals, fibre, phytonutrients, and antioxidants. Think of bananas, mangoes, papayas, apples, pears, oranges, limes, and frozen mixed berries.
- Fibrous veggies are pitifully low in calories but make up for it by being rich in fibre and phytonutrients. Many are rich in nitrates, giving you bigger muscle pumps and increasing muscle growth (study). Think of carrots, spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, beets, and peas.
- Nuts and seeds are rich in healthy fats, protein, and fibre and packed full of micronutrients. Think of walnuts, almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, pistachios, pumpkin seeds, chia, and flax.
- Herbs, spices, and garnish add flavour and nutrients to your meals. Think of garlic, onions, diced tomatoes, pepper, turmeric, oregano, cilantro, mint, hot peppers, and soy sauce.
- Sauces and dips can be nutritious. Think of honey, mustard, nut butter, soy sauce, hot sauce, tahini, homemade mayonnaise, olive oil, vinegar, hummus, salsa, Tzatziki, and guacamole.
- Oils can be grout sources of nutritious fats. Extra virgin olive oil is great for drizzling on salads and veggies. Avocado oil is great for cooking with.
- Coffee and tea are natural sources of caffeine and rich sources of phytonutrients. Just make sure not to have them in the afternoon. It takes many hours for caffeine to clear your system.
How to Sleep for Body Recomposition
Getting good sleep is part of living a healthy lifestyle, with a myriad list of health benefits, ranging from better hormone production to improved willpower and appetite. What many of us don’t realize, though, is that getting enough sleep can help you build muscle faster while burning more fat.

These results are from a study by Jabekk and colleagues (study). The researchers split the participants into two groups. Both groups were put on the same workout program, but only one group was given tips about how to improve their sleep. The group who focused on improving their sleep gained 30% more muscle while simultaneously losing fat.
What I love about this study is the difference came from simple tips. You can follow those same tips and get those same benefits. This brings up the obvious question: how do you improve your sleep?
My sister is a sleep researcher. I spoke with her about this, going over the common tips and how to best implement them. The first thing to focus on is getting to bed on time. Try to go to bed at least 7 hours before you need to wake up. Some guys benefit from as many as 9 hours in bed.
If you’re getting 7–9 hours, you fall asleep within half an hour, you aren’t spending long periods awake during the night, and you wake up feeling refreshed, then you’re all good—you don’t need more. If you do need more—I did—we’ve got a full article on improving sleep for muscle growth.
The Best Supplements for Skinny Fat Guys
Supplements are ridiculously overrated. Even the very best ones pale in comparison to the benefits of lifting weights, exercising, eating a better diet, and getting enough sleep. Still, some can help. I won’t go into depth here, but you can click the links to read our deeper articles.
- Creatine is the best muscle-building supplement. It improves our workout performance, increasing our lean mass and improving our ability to build muscle.
- Protein powder makes it easier to eat more protein. If you aren’t eating enough protein, protein powder is an easy way to get the benefits of eating enough protein.
- Pre-workouts give you more vigour to lift weights. However, they’re only good for people who train early in the day. If you train after work, the caffeine will interfere with your sleep, reducing your energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Bulk When You’re Skinny Fat?
You can bulk when you’re skinny fat. There’s an old bodybuilding myth that having a higher body fat percentage makes it harder to build muscle leanly, but the evidence points the other way. Most research shows that having more body fat makes it easier to build muscle leanly (full research breakdown).
However, if you’re still relatively new to training, your body might be happy to burn body fat to get the energy it needs to build muscle. You might not need to bulk. You might want to wait until you start struggling to make progress in the gym before you worry about eating in a calorie surplus.
If you decide to bulk, we recommend bulking slowly and rigorously, trying to build muscle as leanly as possible.
How Lean Should You Get Before Bulking?
Before bulking, I recommend getting your waist circumference to well under 37 inches (at the height of your belly button). That way, you aren’t gaining so much visceral fat that it starts to harm your health.
You also want to be able to bulk for long enough to build a meaningful amount of muscle. You might gain a little bit of at while bulking, so it helps to have a couple of inches of wiggle room. 35 inches is good.
The bigger issue is getting too lean before bulking. It’s hard to get very lean, and then when you switch to bulking, you may regain a few pounds of fat before you start building muscle again. It’s usually better to bulk at a more moderate body fat percentage (of around 12–20%).
Conclusion
Skinny fatness is defined by being both under-muscled and over-fat, giving you two clear goals to work towards: build muscle and lose fat. The best way to do that is to:
- Follow a good hypertrophy training program. The more muscle growth you can stimulate, the more calories will be invested into muscle growth, and the fewer will be stored as fat. You can even burn some of your body fat to fuel muscle growth.
- Eat enough protein. You can maximize your rate of muscle growth with as little as 0.7–1 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day. There’s no evidence showing a benefit (or harm) to eating more protein than that.
- Eat a good diet. Eat a balanced diet, and try to get at least 80% of your calories from nutritious foods. Think of eating more fruits, veggies, grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, lean meats, fish, and yogurt. Season your food with herbs, garlic, onions, spices, and hot peppers. Drink coffee and tea in the morning. Keep caffeine and alcohol well away from your bedtime.
- Be active. Being active can range from doing cardio to simply going on more walks. For example, you could start by going on a brisk 20-minute walk every morning. Doing more intense cardio can be great, too, but there’s no need to rush into it.
- Get enough good sleep. Sleeping enough every night will give you more energy, motivation, and willpower. It will also improve your hormone profile, allowing you to build more muscle and burn more fat.
When you first start lifting weights, doing more exercise, eating a better diet, and living a healthier lifestyle, you don’t need to worry about calories. Even if your weight doesn’t change, you can expect to build muscle and lose fat, achieving body recomposition.
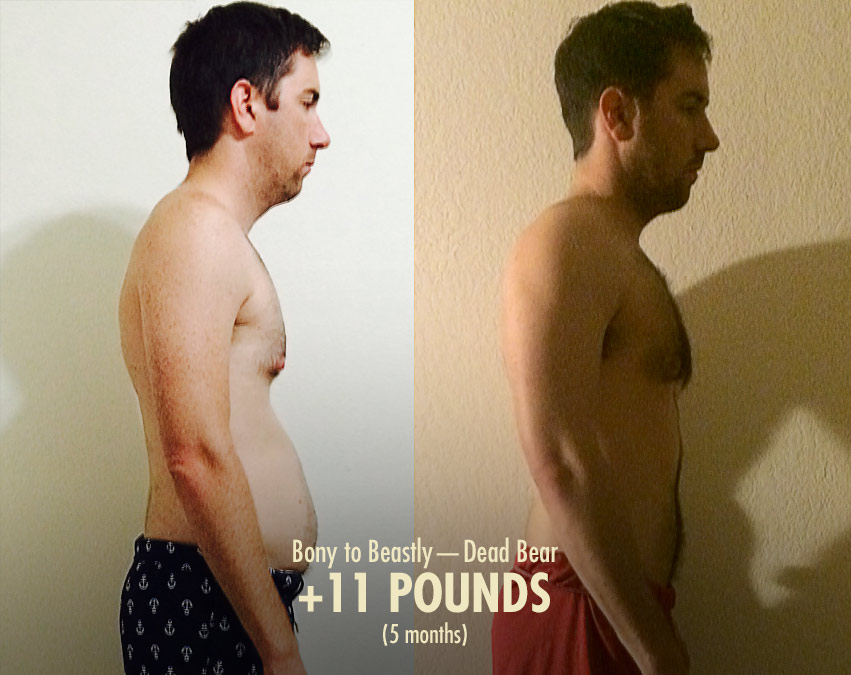

When you stop making progress in the gym, that’s a good sign your muscle growth has plateaued. To continue building muscle, you’ll need to eat more calories, gearing into a lean bulk. Or, if you want to focus on losing more fat, you could eat fewer calories, veering into a cut.
When you bulk, try not to let your waist circumference pass 37 inches. When you cut, don’t get so lean that it feels uncomfortable or unsustainable. It’s often better to aim for a flat stomach instead of chiselled abs. You can try for abs later, once you’re happy with your strength and muscularity.

If you want us to walk you through the process of building muscle and losing fat as a skinny-fat guy, check out our Bony to Beastly Program. It includes a 6-month workout routine, diet guide, recipe book, and online coaching. Or, if you want an intermediate hypertrophy training program, check out our Outlift Intermediate Bulking Program.
If you want the latest and greatest muscle-building information straight to your inbox, we have we have a free newsletter.

