How to Do a Lean Bulk
One of the most common bulking problems is gaining too much fat. For someone already muscular, gaining some fat makes them look beefy. Not a big deal. But for someone still fairly thin, it can make us look skinny fat. Better to do a lean bulk, right?
When you look up how to do a lean bulk, you’ll be told to gain weight very slowly—just a pound or so per month. You might hear about how you need to restrict certain foods or eat a cleaner diet. In some circumstances, that can help.
A better way to build muscle leanly is to stimulate more muscle growth. The more muscle growth you can stimulate, the more calories will be invested in lean mass, leaving fewer to spill over into fat storage. This is especially powerful for us skinny guys, given how quickly we can build muscle.
In this article, we’ll cover why people gain fat while bulking, how to gain muscle faster, how to minimize fat storage, and how to do a proper lean bulk.
What is Lean Bulking?
There are a few different types of bulking:
- Bulking: gaining weight to support muscle growth.
- Dirty bulking: a casual approach to bulking where you lift heavy and eat big, with little regard to the quality of your training, diet, or lifestyle.
- Aggressive bulking: bulking with an emphasis on maximizing muscle growth.
- Lean bulking: bulking with an emphasis on minimizing fat gain. That’s what we’ll cover here.
Everyone who bulks is trying to gain muscle, not fat. That’s what separates bulking from regular weight gain. So keep in mind that even when we’re bulking aggressively—we’re always trying to gain more muscle, less fat.
What separates a regular bulk from a lean bulk is that instead of maximizing muscle growth, the goal is to minimize fat gain. That means gaining weight less quickly and building muscle more slowly, but cutting fat gains way down. Many people prefer this approach, and it’s one of the two paths we recommend in our bulking programs.
Lean Bulking Often Means Tracking Calories
The main disadvantage to lean bulking is it requires precision. There’s a smaller calorie surplus, giving you a smaller margin for error. If you under-eat just a little bit, you won’t have a calorie surplus, so you might struggle to build muscle that day, week, or month. Or it’s possible to overeat one day, gaining more muscle and fat, giving you results similar to a regular bulk.
So what people often do while lean bulking is to track their calories with a calorie-tracking app. That way, they can keep a small, precise daily calorie surplus. If you want to read more about the pros and cons of tracking calories, we’ve written a full article. To make a long story short, you don’t have to track calories while lean bulking, but it helps, and you’ll gain a better intuition about the nutritional contents of food. You won’t be tracking your calories forever, but you’ll keep the wisdom you gained.
If you decide to track your calories, we’re affiliated with MacroFactor, made by Greg and Eric over at Stronger by Science. After reviewing all the calorie-tracking apps, we think MacroFactor offers the most accurate food database, the best algorithm, the best UI, and perhaps most importantly, the best lean bulking recommendations. If you want to try it, you can use the code “b2b” for an extended free trial.
Setting Realistic Lean Bulking Expectations
How Fast Can You Build Muscle?
How fast you can build muscle depends on several factors, ranging from your genetics to how stressful your lifestyle is. But, in our experience, an even bigger factor is how skinny you are. How much room on your frame you have for muscle growth.
According to a study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, the average American man weighs 200 pounds and has 80 pounds of muscle mass. And if you ask most muscle-building experts, most agree that the average man can add around 40 pounds of muscle to his frame, with steadily diminishing returns as he inches closer to his genetic muscular potential. That gives us a chart that looks something like this:
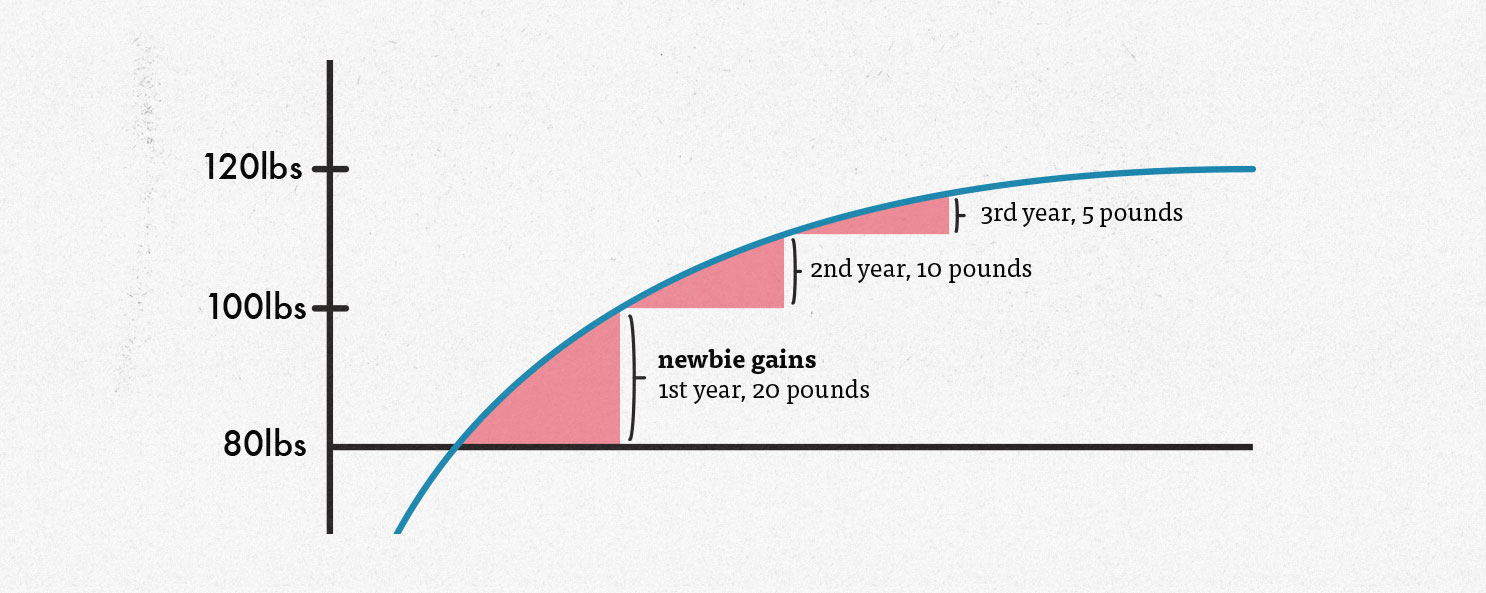
If this graph is accurate, you could expect to gain something like 20 pounds in your first year of bulking up, as you’re getting your “newbie gains.” But I’m not convinced this graph is accurate, especially for skinny guys.
During my first three bulks, I gained 55 pounds with no obvious fat gain. That doesn’t mean I gained pure muscle, just that I finished at about the same body-fat percentage as when I started. While I was doing my second bulk, my roommate (at the time) decided to bulk up with me. He gained 27 pounds in four months, finishing leaner than when he started (full story).
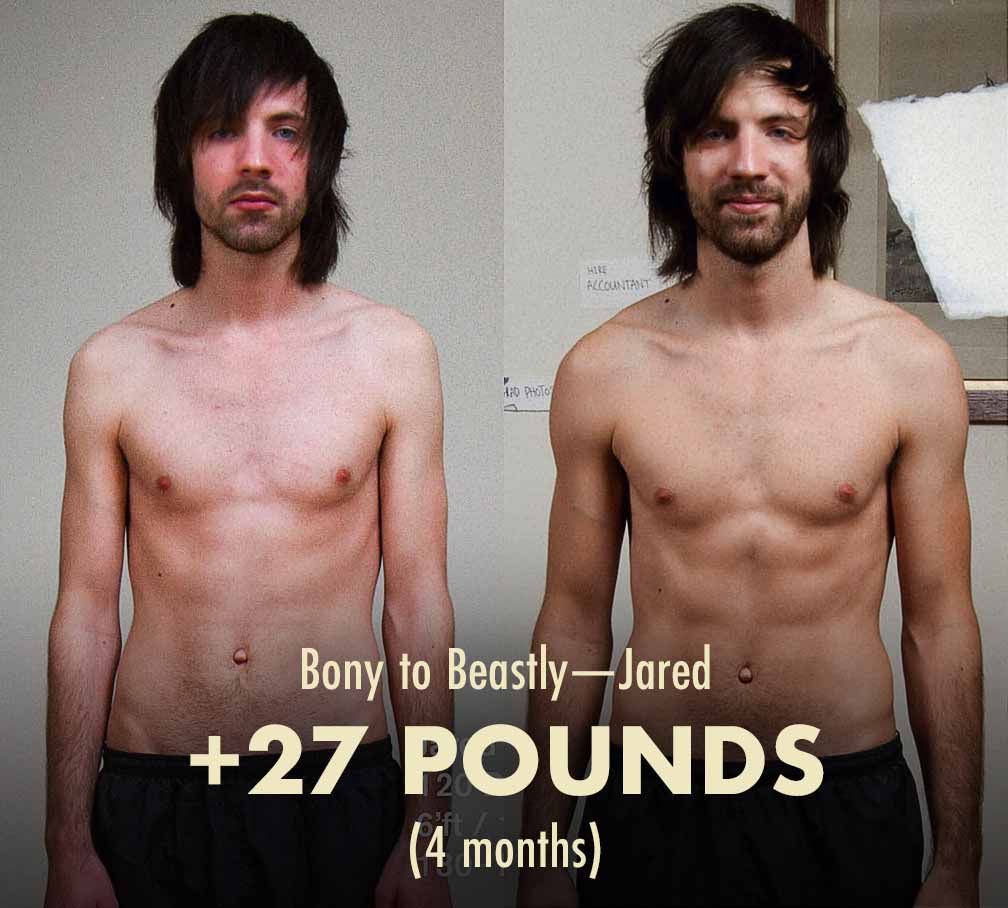

Since then, we’ve helped over ten thousand other skinny guys bulk up. Most people doing our bulking program get comparable results to ours. It seems that skinny guys can bulk much faster and more leanly than the average man.
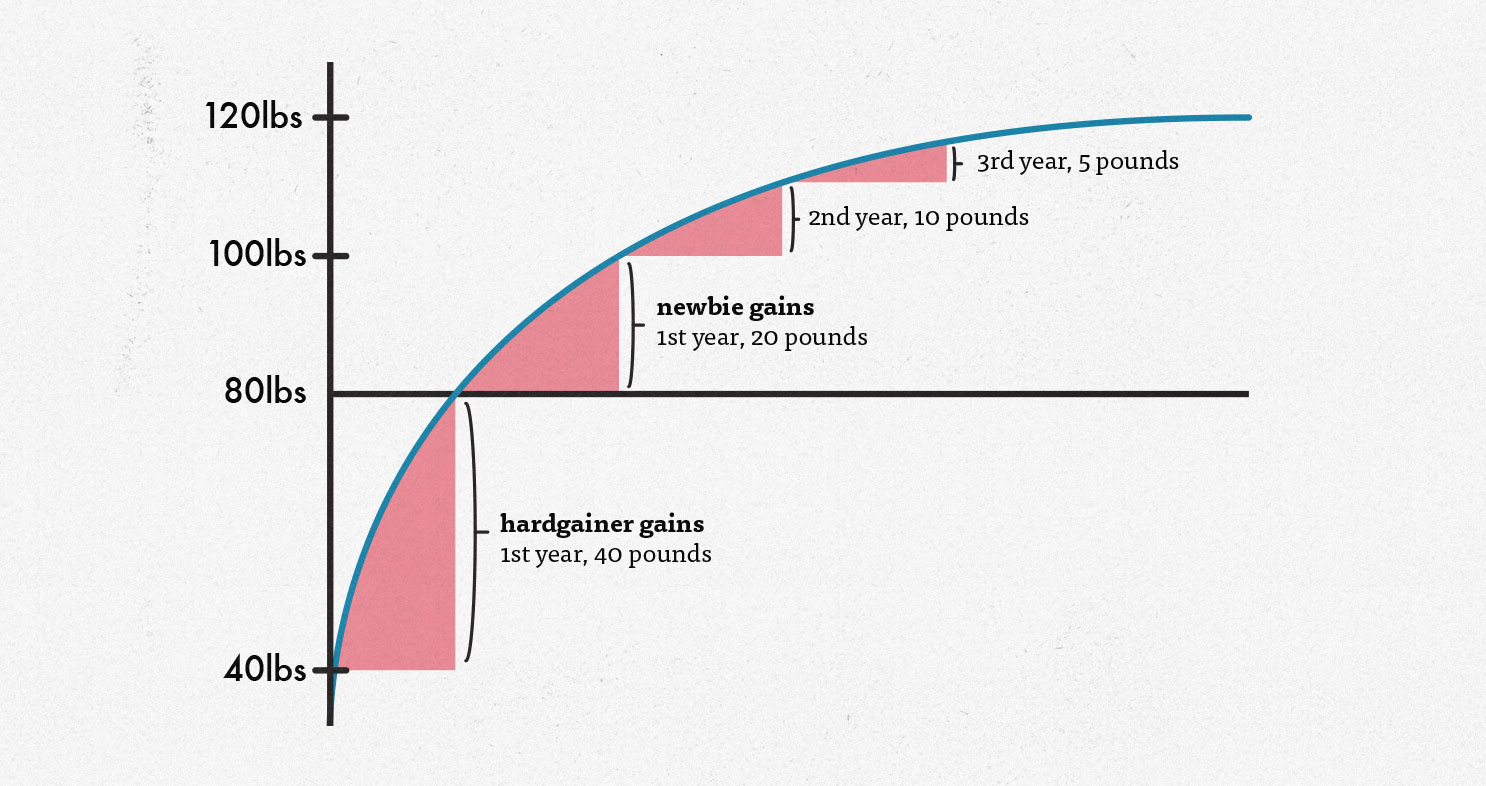
My theory is that we’re further away from our genetic potential, allowing us to build muscle faster until we catch up to where everyone else is starting. For example, if we imagine a skinny guy starting off with half the muscle mass of the average man—40 pounds instead of 80—then we have a guy with far more room for muscle growth on his frame. Maybe that allows him to gain those first forty pounds more quickly and leanly. Or at least that’s what we’ve seen.
The point is, if you’re skinny, you can probably handle a larger calorie surplus and a faster rate of weight gain, even when you’re doing a lean bulk.
Don’t Skinny Guys Have Bad Muscle-Building Genetics?
One common objection is that skinny guys have a reduced potential for building muscle. That our frames can’t hold as much muscle mass. That’s not necessarily true, and even when it is, it’s grossly exaggerated.
Skinniness doesn’t affect our muscle-building potential. However, naturally skinny guys often have narrower frames and thinner bones. That seems to affect our genetic potential. For example, if your wrists are smaller than average, you have less bone mass in your arms to support muscle mass. As a result, you may not be able to bulk up your arms to the same size as a guy with thicker wrists.
To get to the bottom of this, Dr. Casey Butts measured the bone size and muscle mass of various natural bodybuilders. He found that “hardgainers” with smaller frames could only build around 90% as much muscle mass as the average man. And so we adjust our graph accordingly:
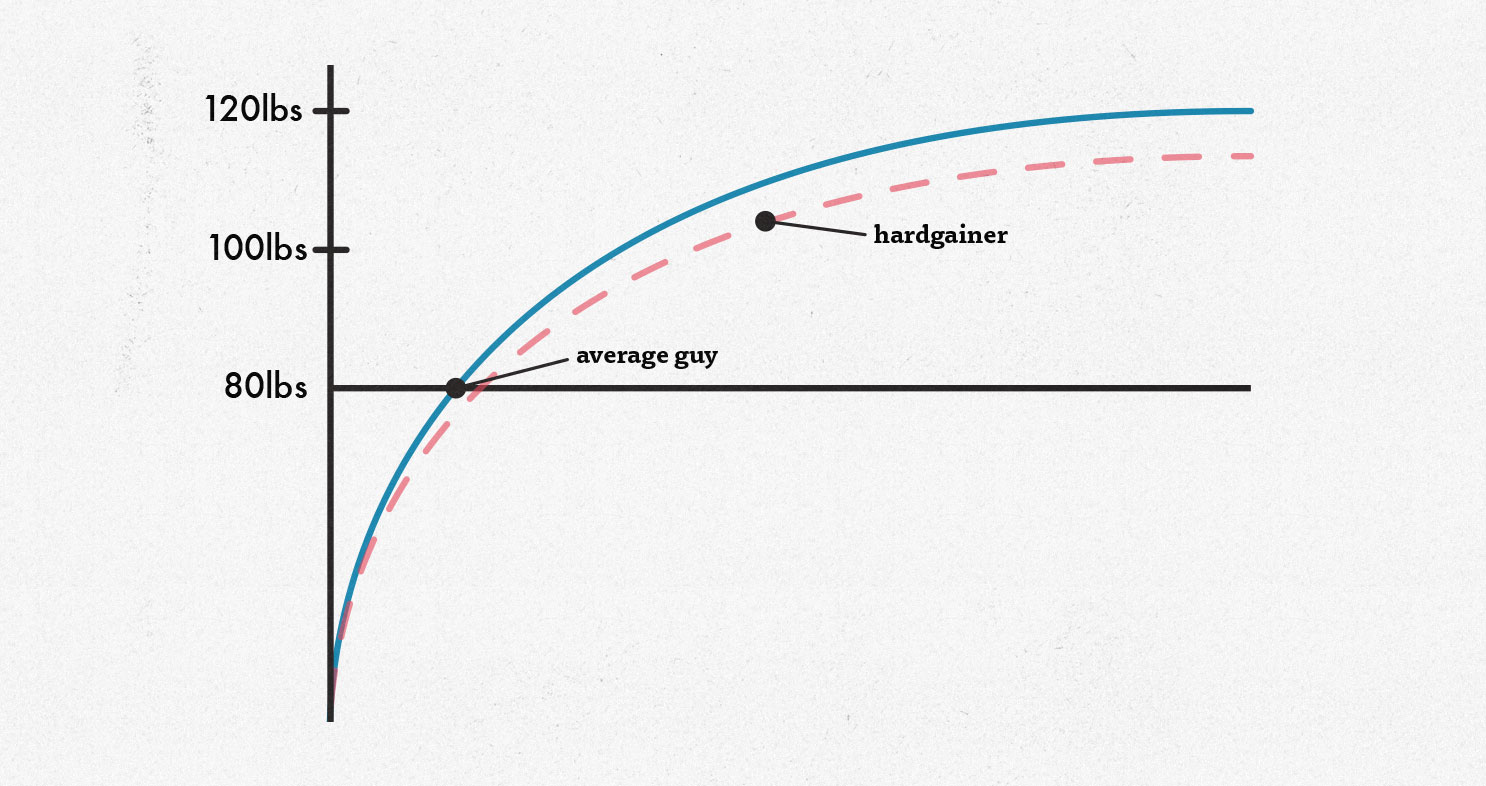
If you’re skinny right now, I wouldn’t assume you have bad muscle-building genetics. I have extremely narrow bones and incredibly small wrists. I assumed I was destined to be smaller and weaker than most other guys. I wondered if it would be possible to bulk up to 150 pounds and bench press 185 before hitting my genetic potential.
All of my worries were for nothing. Once I figured out how to train for muscle growth and eat a good bulking diet, I built muscle quite quickly and leanly. I eventually bulked up to 200 pounds and benched my lifetime goal of 315. More importantly, we’ve seen similar results from thousands of other skinny guys.
How Leanly Can Skinny Guys Build Muscle?
Your ratio of muscle to fat gain while bulking depends on a few different factors. We have to consider your starting point, your experience level, your genetics, how leanly you’re trying to bulk, how good your bulking program is, and how well you follow it.
If you’re skinny and following a good bulking program, you might be able bulk without gaining a visible amount of body fat. Maybe that means gaining 80% muscle and 20% fat, bringing you from 12% to 14% body fat by the end of your bulk. The extra muscle will hide the extra fat, leaving you looking bigger without looking fatter.
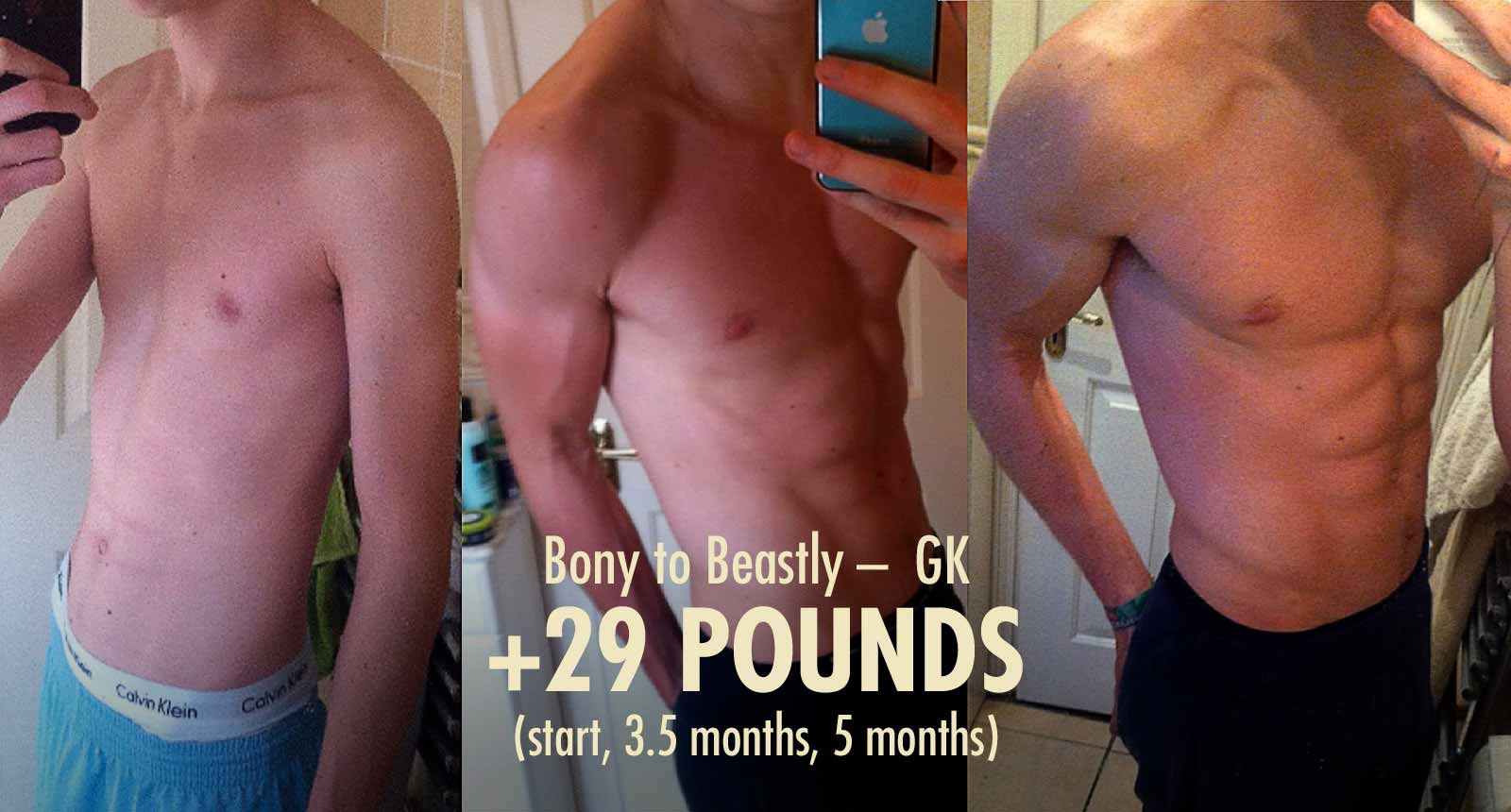
For another example, here’s my second bulk. I’d already gone from 130 to 150 pounds. This shows me going from 150 up to 175 pounds. To do that, I gained around a pound per week on the scale, I followed a good workout program, and I was consistent with my diet and lifestyle. I did gain some fat, but it’s hard to notice.
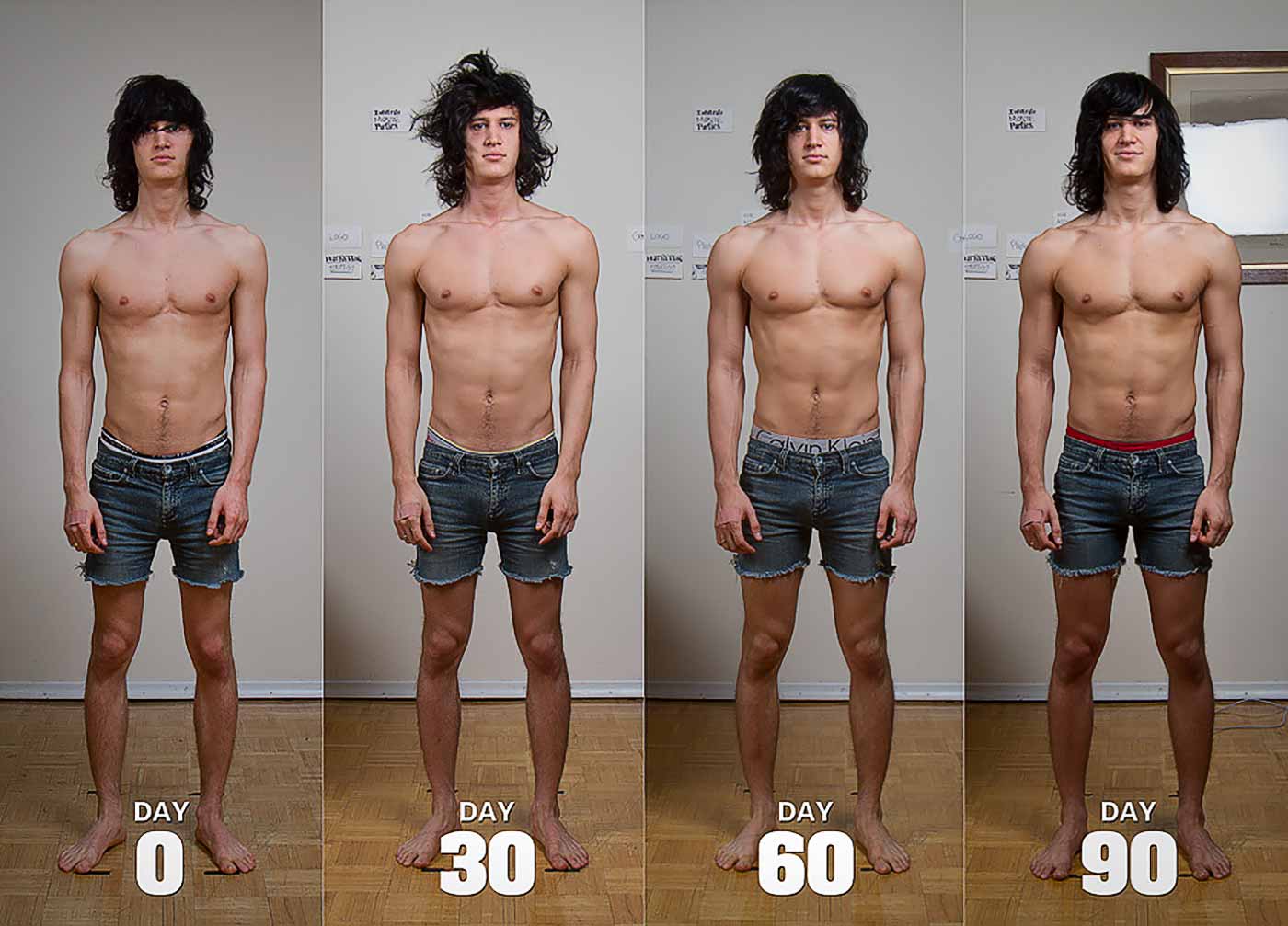

Mind you, we were bulking quite aggressively. If you want to do a lean bulk, I recommend playing it safer. I recommend bulking slower.
How Fast to Gain Weight During a Lean Bulk
Let’s say that you gain 0.5 pounds per week. That might allow you to build muscle leanly, making it great for a lean bulk. But is that enough to maximize your rate of muscle growth? What would happen if you gained weight faster? Would you gain more muscle or more fat?

In our article about how quickly to gain weight while bulking, we cover a recent study comparing guys who gained 1 versus 2 pounds per week. The lean bulking group gained 5 times less fat at the cost of only gaining half as much muscle.
If we look at a systematic review on how quickly we should gain weight to build muscle leanly, we get a recommendation to gain 0.5–1 pound per week. A lean bulk would be on the slower side of that range, meaning you could expect to build muscle even more leanly than these results indicate. At least at first. At least if you’re following a good program.
How to Train for Lean Muscle Growth
The best way to reduce your risk of gaining fat is to combine a good workout routine with a slow rate of weight gain. A good workout will stimulate a ton of growth, making your muscles hungry for calories. Your muscles will gobble up the small calorie surplus, leaving nothing to spill over into fat gain.

Don’t do strength training, a bodyweight fitness routine, or CrossFit. Those are all perfectly good forms of exercise, but they aren’t designed to stimulate muscle growth. They won’t make your muscles hungry enough.
To build muscle quickly and leanly, you should train specifically for muscle growth. Most people call that “bodybuilding,” but that word carries some baggage—thongs, spray tans, too many isolation lifts, and so on. The term we’re looking for is hypertrophy training. Here’s a rough idea of how to do that:
- Choose good exercises: we want to build our routines on a foundation of compound lifts, such as the front squat, bench press, deadlift, overhead press, and chin-up. After that, we can add in smaller lifts to work the muscles that aren’t being fully stimulated, such as our biceps, triceps, side delts, neck muscles, and so on. But those smaller lifts are icing on the cake—most of our growth will come from the big compound lifts.
- Do enough sets per week: most research shows that doing somewhere between 9–18 sets per muscle per week is ideal for building muscle.
- Do enough reps per set: anywhere from 4–40 repetitions per set will build muscle, but we tend to gain more muscle more easily when lifting in the 6–20 rep range. Usually, the big compound lifts are done for lower reps and the lighter isolation lifts for higher reps. For instance, squats for 6 reps, bench press for 10 reps, and lateral raises for 15 reps.
- Rest long enough between sets: we usually need to rest somewhere between 1–5 minutes between sets, allowing us to lift harder in subsequent sets. This allows us to lift more weight overall, stimulating more muscle growth. A good rule of thumb is to let your breathing return to normal before starting your next set.
- Train often enough: to maximize our rate of muscle growth, we want to train our muscles 2–4 times per week. Newer lifters tend to do well with 3 full-body workouts per week, whereas stronger intermediate lifters often benefit from training 4 days per week. But there’s lots of room for personal preference here.
- Train hard enough: to ensure we’re challenging our muscles, we must bring our sets within 0–2 reps of failure on most sets.
- Focus on progressive overload: we don’t need to hit PRs every workout, but we should always try to either add weight to the bar or eke out extra reps. That’s how we achieve progressive overload, becoming bigger and stronger over time.
This might go without saying, but train all your muscles. Most people do bench presses and arm exercises, but make sure you’re also squatting and deadlifting and doing plenty of chin-up and rows. The more muscle mass you stimulate, the more calories your muscles will want, leaving fewer to store as fat.
The Lean Bulking Diet
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Once you’re following a good workout program, the next thing to consider is your protein intake. You need around 0.7 grams of protein per pound bodyweight per day to fully maximize your rate of muscle growth. So if you weigh 150 pounds, you should eat at least 105 grams of protein per day.
It also helps to spread your protein intake out throughout the day, including at least 20 grams of protein in each meal. This fits in well with the idea of eating a nutritious bulking diet. Protein is part of a balanced meal, best paired with carbs, healthy fats, and fibre.
Eat a Nutritious Bulking Diet
The next step is to make sure most of your calories are coming from nutritious foods. You don’t need to eat any one specific food. You certainly don’t need to survive on boiled chicken breast, broccoli, and brown rice drizzled with extra-virgin olive oil. That’s a balanced meal, but there are many others. In fact, most traditional meals are quite healthy, whether that’s stir fry, chili con carne, vindaloo, steak and potatoes, or stew.
Here are the foods to build your lean bulking diet around:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, lean beef): These are excellent sources of protein, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. Meat is also rich in micronutrients. The only downside is that meat fat tends to be high in saturated fat. That’s why it’s usually recommended to eat leaner cuts of meat, especially if you’re eating a lot of it.
- Fish (salmon, tuna, tilapia): Fish is a lean source of protein that also provides healthy omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation and support overall health. This is where you want to get more of your animal fat from.
- Eggs: Eggs whites are a complete protein source. Egg yolks are rich in healthy fats and micronutrients.
- Dairy products (Greek yogurt, kefir, and perhaps cheese): These are good sources of protein and calcium, which are important for bone health. They’re also good sources of probiotics, which is good for digestive health. Note that cheese isn’t always considered clean.
- Whole grains and legumes (such as brown rice, corn, quinoa, oats, beans, lentils, and soy): Whole grains and legumes are a good source of complex carbohydrates, which provide sustained energy for workouts and help support muscle growth. They’re also rich in soluble fibre, which is great for improving blood sugar, blood lipids, and digestion.
- Fruits and vegetables (such as berries, bananas, mangoes, spinach, and broccoli): These provide a wide range of micronutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They’re fantastic sources of insoluble fibre, which is great for general health and digestion. They’re also rich in nitrates, which are good for improving muscle pumps and muscle growth (study). Note that white potatoes aren’t always considered clean.
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds): These are good sources of healthy fats, protein, and fibre. This is one of the best places to get dietary fat.
- Extra-virgin olive and avocado oil: Extra virgin olive oil is great for drizzling on salads and veggies. Avocado oil is great for cooking with. These tend to be the cleanest oils.
- Coffee and tea: These are natural sources of caffeine, and they’re also rich sources of phytonutrients. They tend to be quite healthy. Just watch out not to consume them within a few hours of your bedtime, lest they interfere with your sleep.
You can eat junk food or dessert sometimes. Just remember to keep it in moderation. It needs to fit within your calories. It shouldn’t display too many nutritious foods.
Lean Bulking Macros
You don’t need to track your macros while lean bulking. If you’re tracking your calories with an app like MacroFactor, it will take care of this for you, so you may as well. Otherwise, as long as you’re eating a nutritious diet, eating enough protein, and eating in a small calorie surplus, you’re all good. Your carb and fat macros don’t matter very much.

But if your goal is to absolutely optimize your diet for a lean bulk, here are the ideal macros (study):
- Eat enough protein to maximize your rate of muscle growth. At least 0.7 grams per pound bodyweight per day. This will probably be around 20% of your total calorie intake.
- Get most of your energy from carbs. You can get 40–60% of your calories from carbohydrates. That’s usually around 3–4 grams of carbs per pound of body weight. This will keep your muscles packed full of glycogen, and it will allow you to consume plenty of fibre, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients.
- Fill in the rest of your diet with fats. You should have around 20–30% of your calories coming from fat. This will give you even more micronutrients, and it will help keep your hormones running smoothly.
If you have trouble eating enough calories to gain weight, don’t stress too much about getting your carb and fat macros perfect. Just try to eat a comfortable balance. If you go all the way towards a low-carb, ketogenic diet, not only are you missing out on the muscle-building advantages of carbs, but you may also find it hard to gain weight. The same is true if you try to cut your fat intake too low.
How Often Should You Eat?
People can build muscle with a variety of meal schedules. Some people do LeanGains intermittent fasting, eating 2–3 meals within an 8-hour window. Other people use a classic bodybuilding meal schedule, eating every 3–4 hours. Both of those approaches can work, but for skinny guys who are trying to do a lean bulk, the bodybuilding approach tends to work best.
When we eat a meal that contains enough protein in it—at least 20 grams—we trigger a small burst of muscle growth, like so:
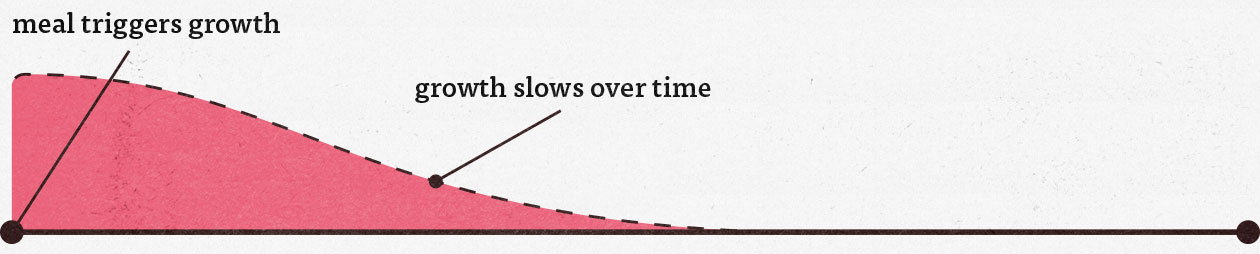
When we’re spreading out our meals over the course of the day, we’re getting plenty of opportunities to eat protein, plenty of opportunities to get our calories in. That allows us to maximize our rate of muscle growth throughout the day, and the faster we can build muscle, the fewer calories are left to spill over into fat gains.
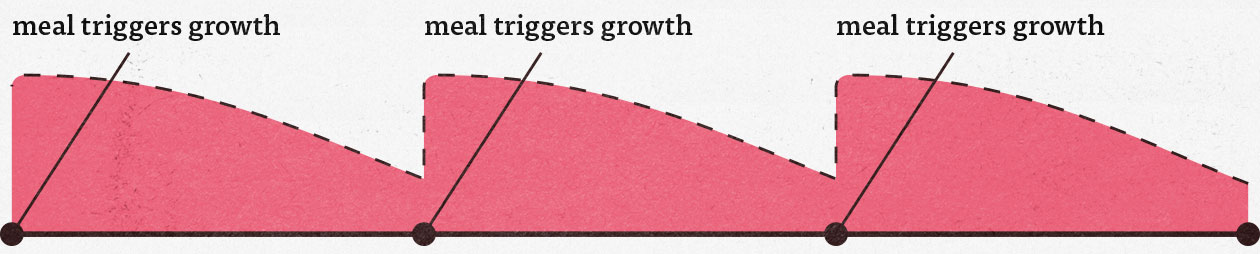
So, how many meals should you eat to fully maximize your rate of muscle growth? 3 meals per day will get you pretty close. 4 meals is probably slightly better. And by eating 5 meals per day, you might get a tiny extra advantage. So for optimal results, aim to eat at least 3 meals per day, and perhaps as many as 5.
Now, with that said, this is a fairly minor factor, and there’s still plenty of room for flexibility. You could eat breakfast, lunch, and dinner, and then add a snack or two. And that’s perfect. It doesn’t need to be more complicated than that.
To summarize, when organizing your meal schedule for a lean bulk, it can help to eat 3–5 meals spread out somewhat evenly over the course of the day. But not all of your meals need to be meals. A smoothie, snack, protein bar, or protein shake will do the trick.
Lean Bulking Supplements
There are a few supplements that can help with building muscle. Of them, the best are creatine, caffeine, and protein. Creatine can speed up your rate of muscle growth, which also allows you to bulk more leanly. Protein powder can make it easier to eat enough protein. And caffeine can help improve your energy levels, motivation, and workout performance.

Mass gainers are popular with skinny guys. They do work, but I’d recommend blending up smoothies instead. That way, you get more micronutrients, fibre, and phytonutrients.
Sample Lean Bulking Meal Plan
There’s no specific diet or meal plan that’s ideal for lean bulking. Still, there are some things you can do to gain muscle faster and more leanly. As a default, we recommend eating 3–5 meals per day (including snacks), having some protein in every meal, and eating plenty of carbohydrates—around 40–60% of the calories you’re eating.
In my case, my lean bulking diet looks like this:
- First thing in the morning: coffee and a Quest bar
- Mid-morning breakfast: a smoothie with yogurt, oats, fruits, nuts, spinach, and protein powder.
- Lunch: leftovers, meat tacos, or some stew.
- Before dinner: 1–2 margaritas or beers.
- Dinner: salmon with broccoli and rice, chili, paella, or pasta.
- Before bed: oatmeal mixed with casein, almond milk, greek yogurt, and blueberries.
This is just what I like to eat. Your diet should be made out of things that you like to eat. Still, there are a few principles I’m thinking about. If you understand how those work, it will be much easier to build a good lean bulking diet.
- The overall amount of food I’m eating is enough for me to gain around 0.5 pounds on the scale each week, which is a good pace for building muscle leanly.
- I’m eating 156+ grams of protein per day (at a weight of 195 pounds), which is enough protein to maximize my rate of muscle growth.
- Each of my 5 meals and snacks has at least 20 grams of protein, which is an ideal protein distribution for building muscle throughout the day.
- Over 80% of my calories come from nutritious whole foods, leaving another 20% of my calories to come from Quest bars and margaritas.
- When I add calories to my diet, I lean towards starchy carbs: fruits, pasta, rice, and oats. That’s where I get most of my extra energy from.
- When thinking of what fats to eat, I already eat some cheese, eggs, and meat, so I try to include more olive oil, nuts, and seafood. That gives me a more balanced fat intake.
Get Enough Good Sleep
Once you’re training for muscle growth and eating a good lean bulking diet, the next thing to look at is your sleep. A recent study found that when lifters were taught how to improve their sleep, they gained muscle 30% faster than the control group:
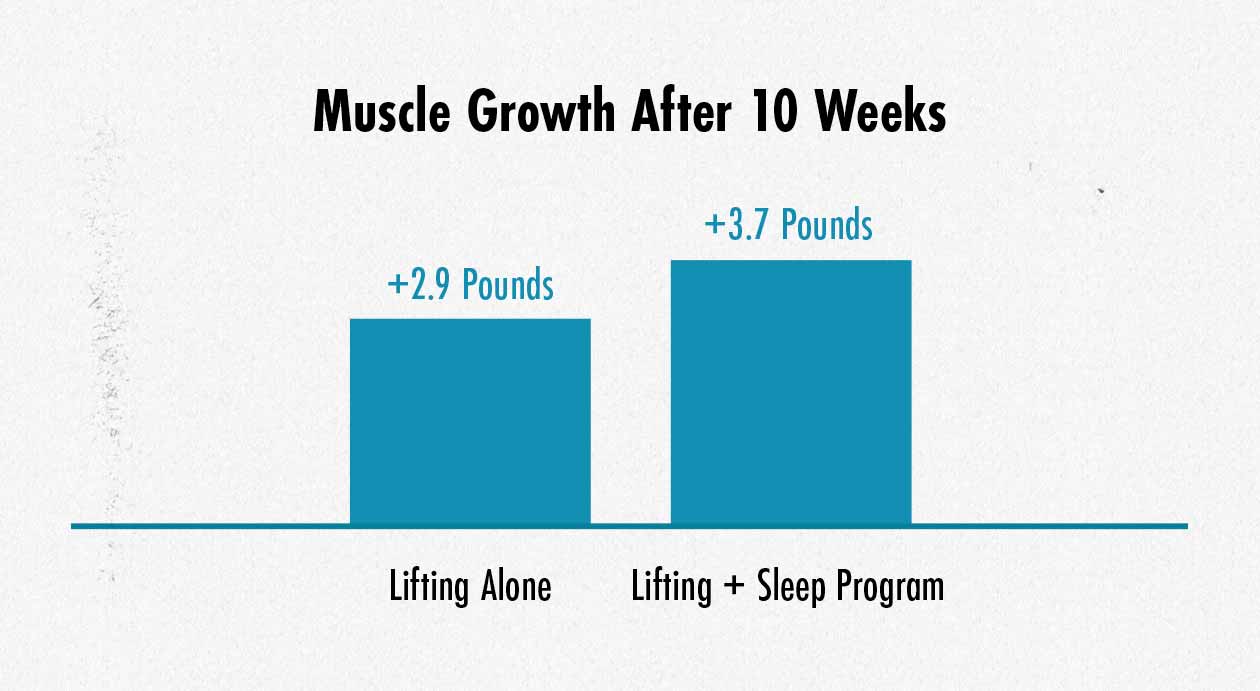
And, of course, more muscle growth at a given rate of weight gain means less fat gain, right? So we’d expect that improving our sleep might allow us to gain 30% less fat. That wasn’t the case. The group who improved their sleep could build more muscle with fewer calories, getting more energy from fat.
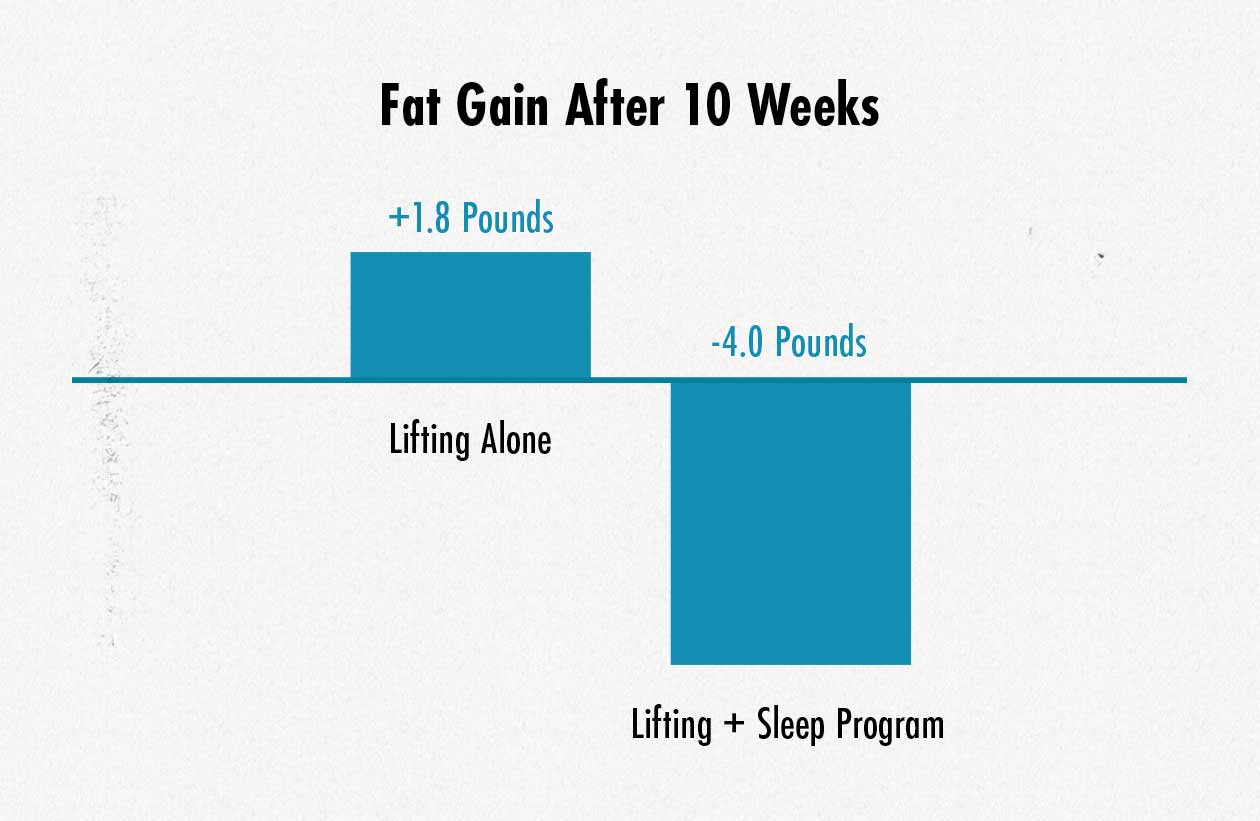
This study isn’t an outlier, either. Previous research found the same increase in muscle growth. And we also see the same effect when people are given supplements that improve their sleep, such as melatonin (study).
Best of all, these participants weren’t put in a sleep lab, they were just given a few simple instructions about how to get better sleep:
- Get enough sleep: 7–8 hours is enough for most people. I recommend giving yourself 8–8.5 hours and then seeing if you wake up early. Then, if you find that you’re routinely waking up after 7 hours feeling refreshed, great. Switch to 7 hours.
- Get better quality sleep: the next thing is trying to get deep, restful sleep without waking up more than once per night. Dimming the lights in the evening and doing something relaxing in the hour leading up to your bedtime can help a great deal.
We can go much deeper on how to improve your sleep, though, and each of these points has some nuance. If you want more, check out our article on improving sleep for lean muscle growth.
Live a Healthy Lifestyle
The next thing to consider is that you aren’t living an unbalanced or unhealthy lifestyle. We’ve covered all of the major points of training, diet, and sleep, but that doesn’t account for all of the other things in your life.
- Are most of your calories coming from whole foods?
- Are you limiting yourself to 0–2 margaritas per day?
- Do you spend some time being active, such as doing cardio, playing sports, or going on daily walks?
- Are you regularly getting outside and getting some sun? And if not, have you checked your vitamin D levels?
- Are you managing your overall stress okay? Stress is fine, but make sure you’re exercising, getting enough sleep, and feeling a sense of purpose.
We have a full article on how to bulk the healthy way.
Summary
There are plenty of tips and tricks that you can use to bulk up leanly. But the best way to minimize fat gain while bulking is to focus almost all of your energy on the fundamentals:
- Choose a good hypertrophy workout routine, follow it consistently, and bring your best effort to each rep of each set, especially on the big compound lifts. Your workouts should be challenging, with your sets brought within a rep or two of muscular failure. And you should be fighting to outlift yourself, trying to add weight to your lifts or eke out extra reps.
- Eat enough protein, aiming to get at least 0.8 grams of protein per pound bodyweight per day. For a 170-pound guy, that’s at least 136 grams of protein per day. And try to spread that protein out between your meals and snacks, with at least 20 grams every time you eat. Bonus points if you eat 4–5 meals per day (including snacks).
- Get enough sleep, setting aside at least 8 hours in bed each night, at least until you get into the habit of waking up before your alarm clock. And the quality of your sleep matters, too. Try to ease into sleep with a relaxing bedtime routine so that you fall asleep faster and sleep more deeply.
- Live a healthy lifestyle, keeping your drinking and stress under control, getting most of your calories from whole foods, getting outside on a daily basis, and engaging in physical activity, such as walking, sports, or cardio.
- Don’t gain weight too fast! If you’re doing the above points correctly and gaining too much fat, it’s probably because you’re gaining weight too quickly or inconsistently. Aim for 0.5 pounds per week.
Try to build muscle leanly, but remember to bulk with confidence. If you notice some fat gain, adjust what you’re doing, but keep moving forward. Keep adjusting and pivoting as you build more and more muscle. That’s what bulking is all about.

Alright, that’s it for now. If you want more muscle-building information, we have a free bulking newsletter for skinny guys. If you want a full foundational bulking program, including a 5-month full-body workout routine, diet guide, recipe book, and online coaching, check out our Bony to Beastly Bulking Program. Or, if you want a customizable intermediate bulking program, check out our Outlift Program.

