Articles
Lifting With Momentum is Good, Actually
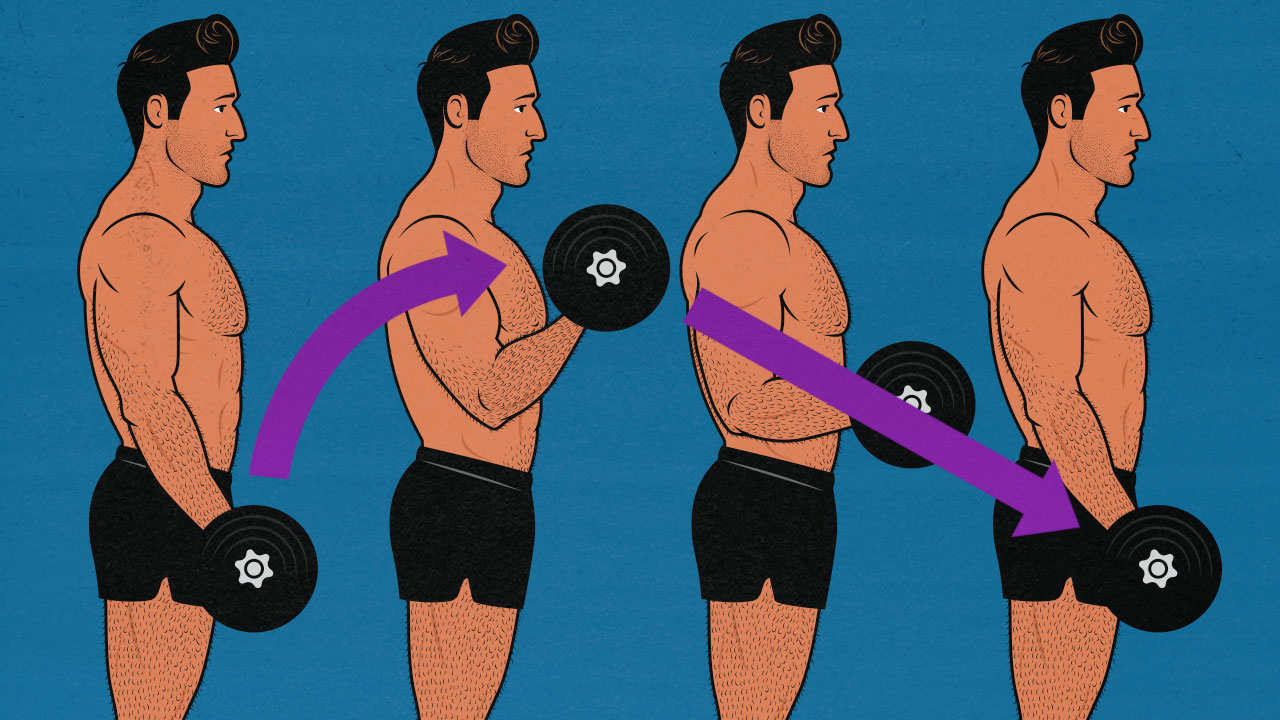
Lifting with momentum has a bad reputation, especially among bodybuilders. The concern is that if you lift explosively, or if you cheat, or heave, or swing, then you’ll make some parts of the lift too easy on the muscles you’re trying to train. I disagree with that idea, but there is a small grain of truth there. Sometimes.
What’s rarely mentioned, though, is how if you use momentum wisely, it can help you gain more strength, athleticism, and even muscle mass.
Read MoreHow Fast Should You Lift & Lower Weights?
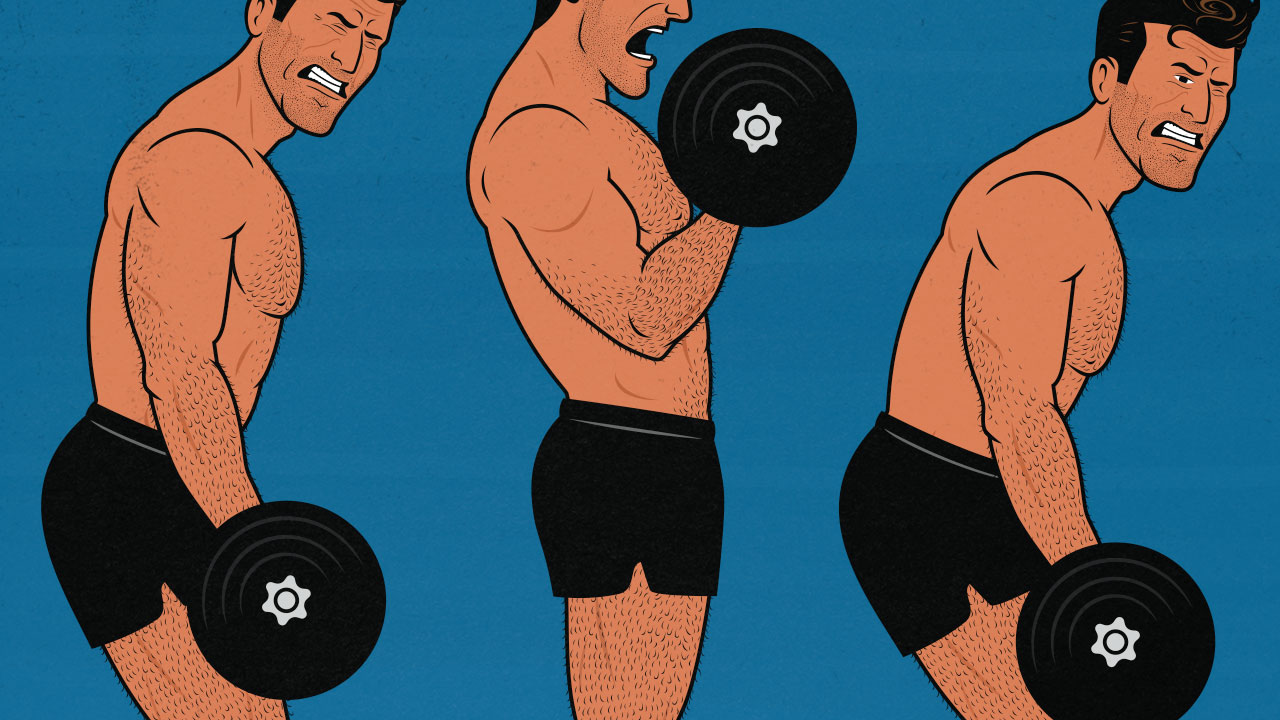
If you lift weights slowly, you can keep tension on your muscles for longer, but you won’t be able to lift as heavy.
If you lift weights with a normal tempo, you can lift more weight, but you won’t be keeping tension on your muscles for as long.
If you lift weights fast, you’ll engage more muscle mass and increase your performance, but you’ll also increase momentum, and it will be harder to maintain a strong mind-muscle connection.
So, how fast should you be lifting and lowering weights? And how should your lifting tempo change if you’re training for strength, athletic performance, or muscle size?
Read MoreHow Does Arching on the Bench Press Affect Muscle Growth?
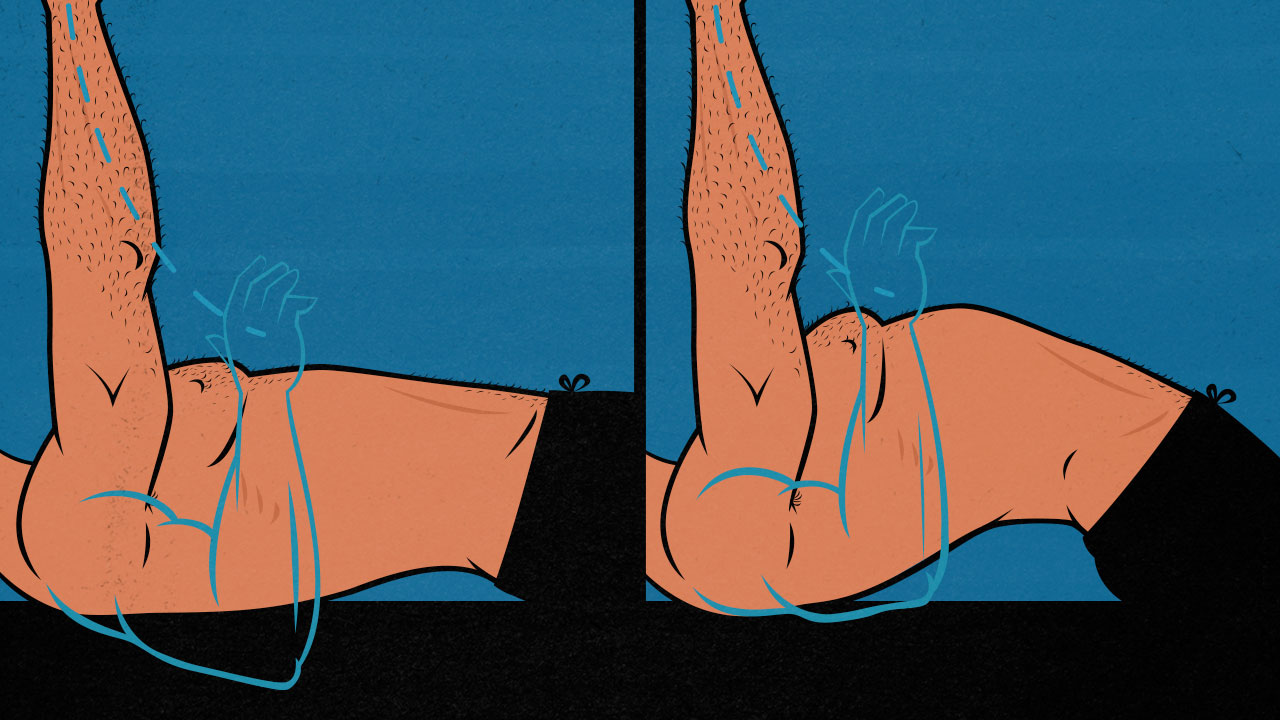
Most people arch when they do the bench press, especially if they come from a strength training or powerlifting background. It shortens the range of motion and gives our shoulders better leverage, allowing us to push more weight. But what if you aren’t a powerlifter? What if you aren’t just trying to move more weight, you’re also trying to build more muscle? Should you be arching? Or does it turn the bench press into more of a decline press, biasing your lower chest, leaving your upper chest high and dry?
A new study by Cudlip and colleagues compared muscle activation when benching with a neutral spine versus benching with an arched back. It looked into back and triceps activation, as well as upper and lower chest activation.
So, what did they find? How does arching your back affect muscle growth when benching?
Read MoreAthlean-X Says One-Arm Rows Cause Hernias. Do They Really?
In one of Athlean-X’s latest videos, Jeff Cavaliere makes the argument—again—that the one-arm dumbbell row is the worst back exercise. He argues that if you put an asymmetrical strain on your groin, it can give you a hernia. And so, because the one-arm dumbbell row uses an asymmetrical stance, it causes hernias. But is any of that actually true?
The dumbbell row is a popular lift. So are other lifts that asymmetrical strain our groins, such as split squats and landmine presses. None of these lifts have a reputation for causing injuries of any kind, let alone hernias. But smoking was popular, too, and look where that went. So who knows. Maybe a quiet killer has been hiding in your workout routine all along, waiting for the right moment to stab you in your side.
If you want to build muscle, you seek out a strength coach. And that’s no problem. That’s what Marco does best. He’s even had similar clients to Athlean-X, including college, professional, and Olympic athletes. But he’s not a physiotherapist. He wasn’t focused on their prehab and rehab. He was tasked with bulking them up. He’s not afraid of dumbbell rows causing hernias, and after a decade working as a strength coach, he’s never seen it happen. But it’s also slightly outside of his area of expertise.
So I reached out to Greg Nuckols, who connected us with Dr. Jason Eure, DPT. Not only does Jason have a similar education to Athlean-X, but his education is more current, and it’s technically one notch higher. Jeff Cavaliere has a Master’s degree in physical therapy (MPT), whereas Jason is a full doctor (DPT). Plus, he’s a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist (CSCS), and he’s coming from Stronger by Science, which is about as reputable a source as you can get in the fitness industry.
We asked him: are one-arm dumbbell rows dangerous? Can they cause hernias?
Read MoreShould You Track Calories While Bulking?
If you ask a bulking guru if you should track calories while bulking, you’ll probably get one of two answers:
- If you’re serious about building muscle, you need to Police your calorie intake: You need to track every breath you take, every move you make, every vow you break, every single day, every word you say, every game you play, every night you stay. That’s the only way to figure out how many calories you’re burning and how many you should eat. And figuring that out is the only way to build muscle quickly and leanly.
- The second answer is a pushback against that mindset: don’t be so obsessive! You aren’t a bodybuilder. You don’t need to adopt a disordered eating routine to get great bulking results. Just eat intuitively, eat healthy foods, and get in touch with your appetite. You don’t need to track everything. And besides, tracking calories is always imprecise. There’s just no way around it. Nutrition labels are off by like 40%. You’ll never know exactly how many calories you’re eating or burning. Why even bother?
Both of those answers make some good points. Mind you, most gurus arguing against calorie-tracking apps aren’t victims of those apps, they’re beneficiaries. They benefitted from using calorie trackers while bulking. And now, with the very best of intentions, they’re kicking out the ladder that would allow you to catch up to them. In this article, we’ll teach you how to catch up to them.
But on the other hand, you don’t need to track your calories to get great bulking results. There are other ways to eat (roughly) the right number of calories every day. We’ll teach you how to do that, too. It’s not as impossible as it might seem.
Dive Into itWhat Happens if You Don’t Eat Enough Protein While Bulking?
Your muscles aren’t made of just protein. They’re actually around 76% water (study). That isn’t to say protein isn’t important. It is. It’s just that since only a small portion of your muscles are made of protein, you actually don’t need to eat that much extra protein to maximize your rate of muscle growth.
The bottleneck for muscle growth is often energy—calories—not your protein intake. If you’re fairly lean or skinny, the best thing you can do to build muscle faster is to stimulate more growth in the gym and then eat more food.
In fact, if you aren’t eating enough calories to gain weight, you may not be able to gain any muscle at all. It can completely halt your muscle growth. If you’re lifting weights and gaining weight, though, you should be able to build muscle just fine, even if you aren’t optimizing your protein intake.
With all of that said, the contractile tissue in your muscles is made of protein. Protein does matter. Plus, you also need protein for the rest of your organs, your hair, nails, and all manner of bodily functions. Eating enough protein is part of eating a balanced diet, and hitting your minimum protein targets will indeed allow you to build muscle faster.
But how much does protein help? And what happens if you don’t eat enough?
Read MoreIs the 3/7 Method Good for Building Muscle?
How Many Carbs Should You Eat to Build Muscle?
Bodybuilders traditionally eat high-carb diets while bulking, getting anywhere from 50–60% of their calories from carbohydrates. Carbs are a great source of calories, they can be relatively easy to digest, they’re rich in nutrients, and they’re fantastic for building muscle.
In this article, we’ll talk about the benefits and downsides of eating so many carbs, cover the latest research, and then give you some modern recommendations.
Delve DeeperAre You Lean Enough to Bulk?
Let’s say you’re a skinny guy eager to build muscle. But you aren’t lean. You don’t have much muscle definition. No abs. Maybe you’re even “skinny-fat.” Are you lean enough to bulk? After all, even if you do a lean bulk, you may still gain some fat. That can be stressful if you’re already feeling too soft.
Plus, many bodybuilders believe that when your body-fat percentage gets too high, it interferes with bulking. Testosterone converts into estrogen, insulin sensitivity crashes, it gets harder to build muscle, and you gain proportionally more fat. Is any of that true?
How can you know if you’re lean enough to bulk?
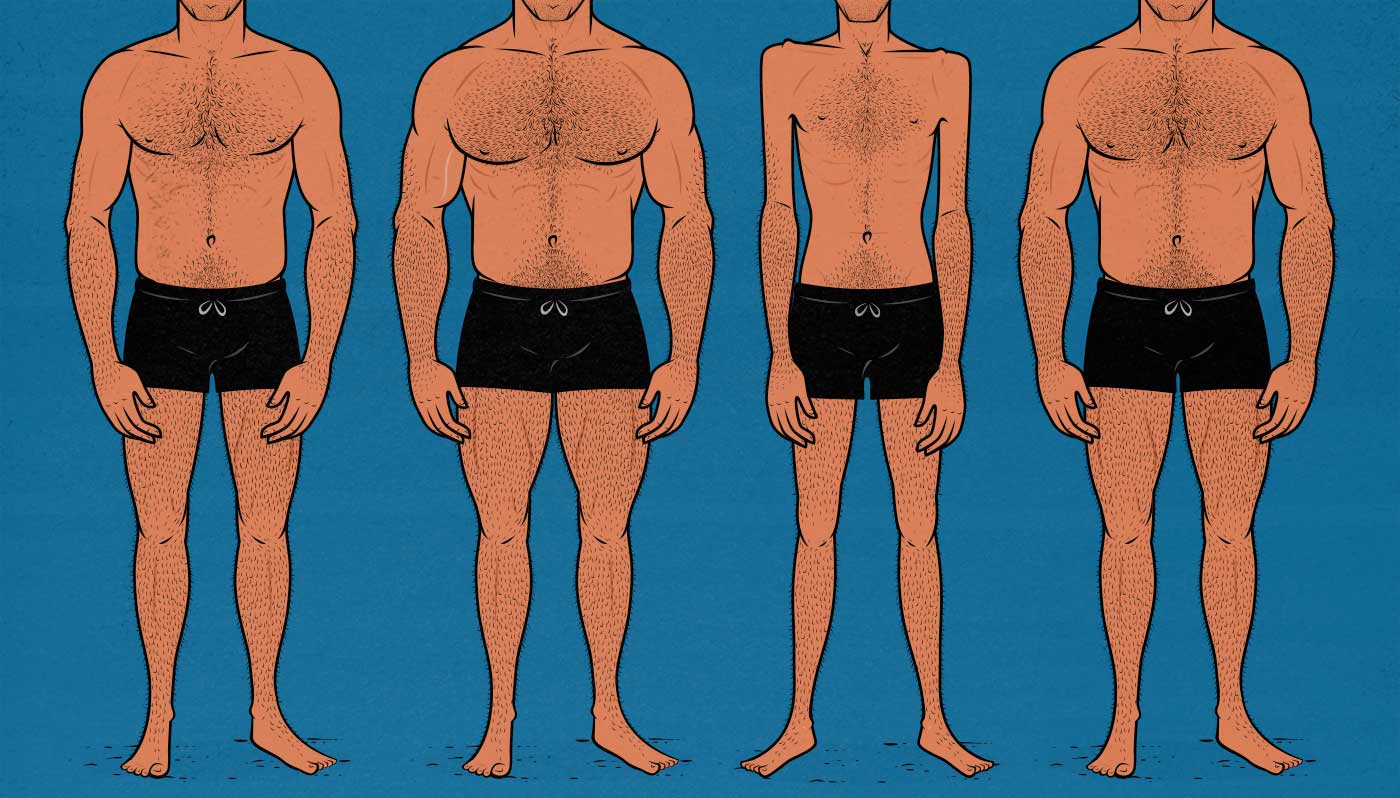
Read MoreThe Ideal Male Body Type According to Women (Survey Results)
I surveyed 423 women, asking them to rate different body proportions and levels of muscularity and leanness in men. To do that, I traced my body and then adjusted the proportions, leanness, and muscle sizes. I tried to answer questions like:
- What’s the most attractive amount of muscle for a man to build?
- Do women prefer more muscular upper bodies or lower bodies?
- What proportions do women find most attractive?
- What’s the most attractive body fat percentage?
- Which muscles do women find most attractive?
- Does neck size affect our appearance?
- What’s the most attractive overall body type?
Here are the survey results.
Read More